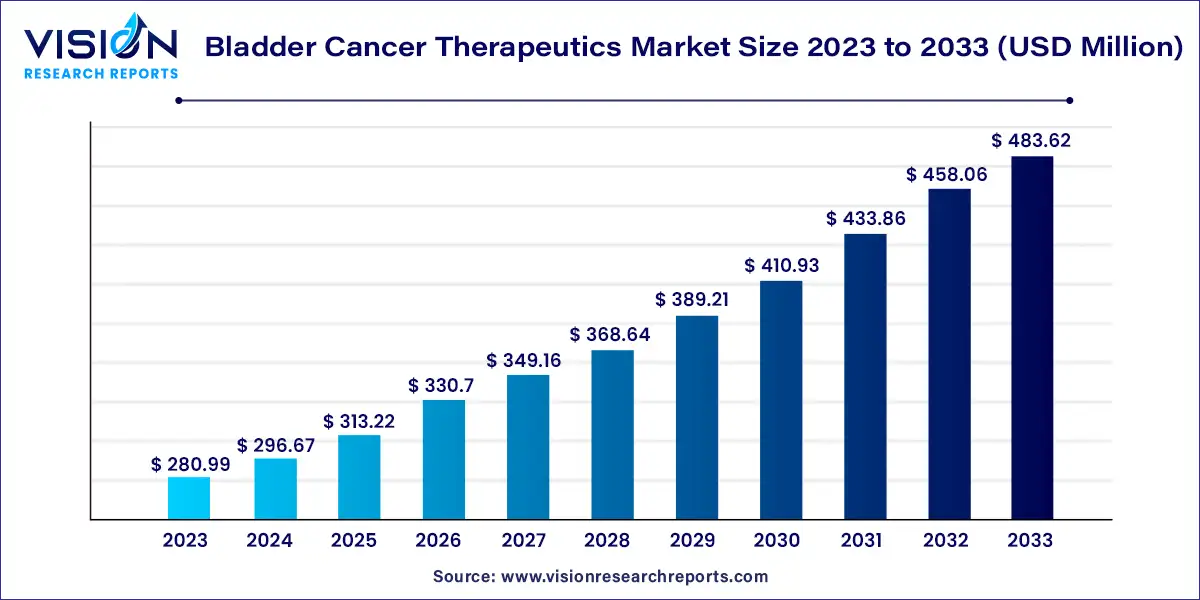
The global bladder cancer therapeutics market size was estimated at around USD 280.99 million in 2023 and it is projected to hit around USD 483.62 million by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 5.58% from 2024 to 2033.
The global bladder cancer therapeutics market is witnessing substantial growth owing to several factors, including the increasing prevalence of bladder cancer, advancements in medical technology, and the development of innovative therapeutic approaches. Bladder cancer is a significant public health concern, with a rising incidence rate globally. It is essential to understand the market dynamics, key players, treatment modalities, and market trends shaping the bladder cancer therapeutics market.
The growth of the bladder cancer therapeutics market is propelled by several key factors. Firstly, the increasing prevalence of bladder cancer cases worldwide, attributed to factors such as aging populations and environmental influences, drives the demand for effective treatments. Secondly, advancements in medical research, particularly in immunotherapy and targeted therapy, have revolutionized bladder cancer treatment, offering patients more promising and personalized therapeutic options. Additionally, heightened awareness campaigns and early diagnosis initiatives have led to a growing number of diagnosed cases, necessitating the development and adoption of innovative therapeutics.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2023 | USD 280.99 million |
| Market Revenue by 2033 | USD 483.62 million |
| Growth Rate from 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 5.58% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024 to 2033 |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units)Companies Covered |
Transitional cell bladder cancer, also known as urothelial carcinoma, is the most common type of bladder cancer. It originates in the urothelial cells, which line the bladder. This type of bladder cancer tends to start as non-invasive tumors, often limited to the surface of the bladder lining. Patients with non-invasive transitional cell bladder cancer typically have a relatively good prognosis, especially if the cancer is diagnosed and treated at an early stage.
Invasive bladder cancer refers to cancer that has penetrated the muscular wall of the bladder and has the potential to spread to nearby organs and lymph nodes. Invasive bladder cancer is a more aggressive form of the disease and requires prompt and intensive treatment. Patients with invasive bladder cancer often undergo surgical procedures to remove the affected portion of the bladder, followed by chemotherapy or immunotherapy to target any remaining cancer cells.
Hospitals, being the cornerstone of healthcare services, offer a wide array of resources and specialized medical professionals to diagnose, treat, and monitor bladder cancer patients. They provide a range of services, from initial diagnostic tests and surgical procedures to chemotherapy sessions and post-treatment follow-ups. Hospitals often house oncology departments with experienced oncologists and surgeons who specialize in bladder cancer, ensuring that patients receive expert care and personalized treatment plans tailored to their specific needs.
Specialty clinics, on the other hand, cater to the specific requirements of bladder cancer patients, offering focused and specialized services. These clinics are dedicated centers staffed with healthcare professionals specializing in urology and oncology. Patients visiting specialty clinics benefit from the expertise of urologists, oncologists, and other specialists who focus exclusively on bladder cancer. These clinics often have advanced diagnostic equipment and treatment facilities, enabling precise diagnosis and targeted therapies.
Cystectomy, a surgical procedure, involves the removal of part or the entire bladder affected by cancer. It is a crucial treatment option, especially for invasive bladder cancer cases where the cancer cells have penetrated the bladder's muscular wall. During a cystectomy, the surgeon may also remove nearby lymph nodes and other affected tissues to prevent the spread of cancer. Following the removal of the bladder, patients undergo urinary diversion procedures to ensure the continuity of urinary function. Cystectomy is often considered in cases where other treatments have proven ineffective or when the cancer has reached an advanced stage.
Chemotherapy is a systemic treatment approach that utilizes drugs to kill or inhibit the growth of cancer cells. In the context of bladder cancer, chemotherapy can be administered before surgery (neoadjuvant chemotherapy) to shrink tumors and make surgical removal easier. It can also be used after surgery (adjuvant chemotherapy) to eliminate any remaining cancer cells or as the primary treatment for patients who are not candidates for surgery. Chemotherapy may involve a combination of drugs, and the specific regimen is determined based on the patient's overall health, the stage of cancer, and the presence of any underlying medical conditions.
Cystoscopy is a crucial diagnostic procedure wherein a thin, flexible tube equipped with a light and camera, known as a cystoscope, is inserted into the urethra and advanced into the bladder. This allows healthcare professionals to visually inspect the interior of the bladder lining for abnormalities such as tumors, inflammation, or other signs indicative of cancer. Cystoscopy not only aids in diagnosing bladder cancer but also enables physicians to determine the stage and extent of the disease. This procedure is especially vital in cases where patients exhibit symptoms like blood in urine, frequent urination, or pain during urination, prompting further investigation for a definitive diagnosis.
Complementing cystoscopy, biopsy serves as a definitive diagnostic tool for bladder cancer. During a biopsy, a small sample of bladder tissue is extracted and examined under a microscope by a pathologist. This microscopic analysis helps in confirming the presence of cancer cells, determining the type of bladder cancer, and assessing the aggressiveness of the disease. Biopsies are often performed during cystoscopy, where suspicious-looking tissues are carefully sampled to provide a precise diagnosis.
Retail pharmacies, often located within local communities, serve as accessible points of contact for patients seeking prescribed medications. Patients can obtain their bladder cancer therapeutics from retail pharmacies conveniently, allowing them to adhere to their prescribed treatment regimens without the need for extensive travel or long waiting times. Pharmacists in retail settings play a crucial role in patient education, ensuring that individuals understand the proper usage, dosage, and potential side effects of their prescribed medications.
The hospital pharmacies operate within healthcare facilities, providing a seamless link between healthcare professionals and patients. Hospital pharmacies are equipped to handle a wide range of medications, including specialized therapies for bladder cancer. These pharmacies are integral in the distribution of intravenous medications, chemotherapy drugs, and other treatments that are administered under medical supervision. Hospital pharmacists collaborate closely with oncologists, urologists, and other healthcare providers to ensure the accurate preparation and administration of bladder cancer therapeutics, especially in cases where treatments require precise dosage calculations or intravenous delivery.
In developed regions like North America and Europe, extensive investments in healthcare, advanced research facilities, and high awareness levels among the populace contribute to the growth of the bladder cancer therapeutics market. North America, in particular, benefits from robust research and development activities, leading to the introduction of innovative treatments. Moreover, favorable reimbursement policies in these regions enhance patient access to advanced therapies, fostering market expansion.
Asia-Pacific, with its large population base, presents both challenges and opportunities in the bladder cancer therapeutics market. Rising healthcare expenditure, increasing awareness, and improving healthcare infrastructure drive market growth in countries like China, Japan, and India. However, the prevalence of bladder cancer in certain regions poses a significant healthcare burden, necessitating effective strategies for early detection and treatment.
By Type
By End-Users
By Treatment
By Major Tests
By Distribution Channel
By Region
 Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
 Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
 Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
 Country/Region-specific Report
Country/Region-specific Report
 Go To Market Strategy
Go To Market Strategy
 Region Specific Market Dynamics
Region Specific Market Dynamics Region Level Market Share
Region Level Market Share Import Export Analysis
Import Export Analysis Production Analysis
Production Analysis Others
Others