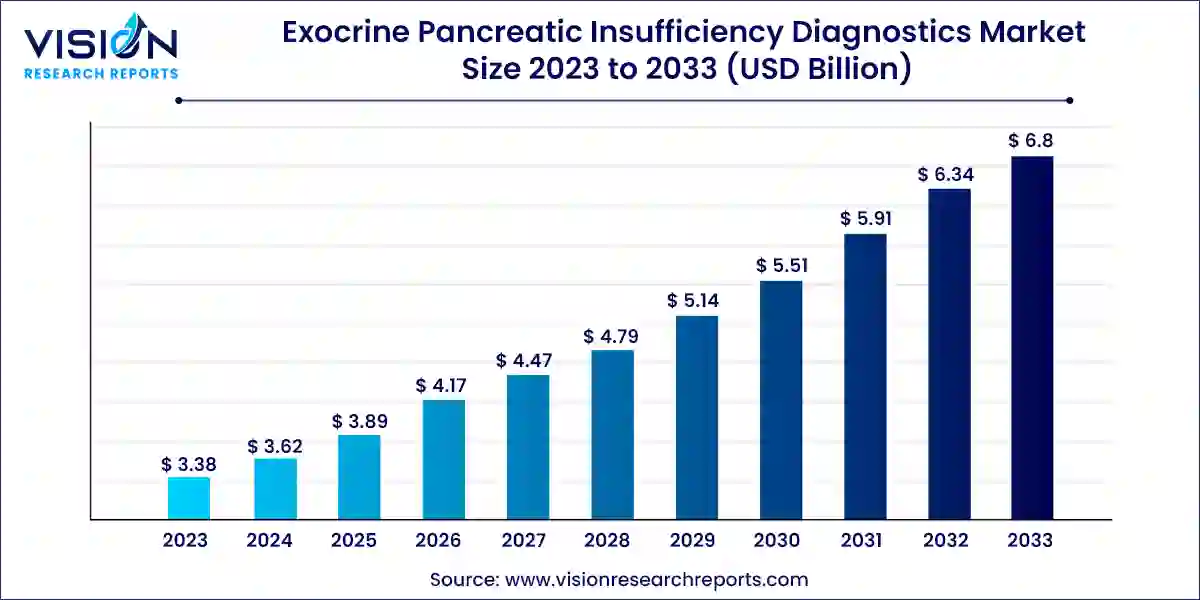
The global exocrine pancreatic insufficiency diagnostics market size was estimated at USD 3.38 billion in 2023 and it is expected to surpass around USD 6.8 billion by 2033, poised to grow at a CAGR of 7.24% from 2024 to 2033.
Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency (EPI) is a condition characterized by the pancreas's inability to produce and secrete sufficient digestive enzymes into the gastrointestinal tract, leading to malabsorption of nutrients. In recent years, advancements in diagnostic techniques have revolutionized the detection and management of EPI.
The growth of the exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI) diagnostics market is fueled by various factors contributing to its expansion. Firstly, an increase in the prevalence of pancreatic disorders, including chronic pancreatitis and cystic fibrosis, has heightened the demand for accurate diagnostic tools to identify EPI early on. Secondly, advancements in diagnostic techniques, such as fecal elastase testing and pancreatic function tests, have significantly enhanced the accuracy and efficiency of EPI diagnosis, driving market growth. Additionally, rising awareness among healthcare professionals and patients about the importance of early detection and management of EPI has led to a greater adoption of diagnostic tests, further boosting market demand.
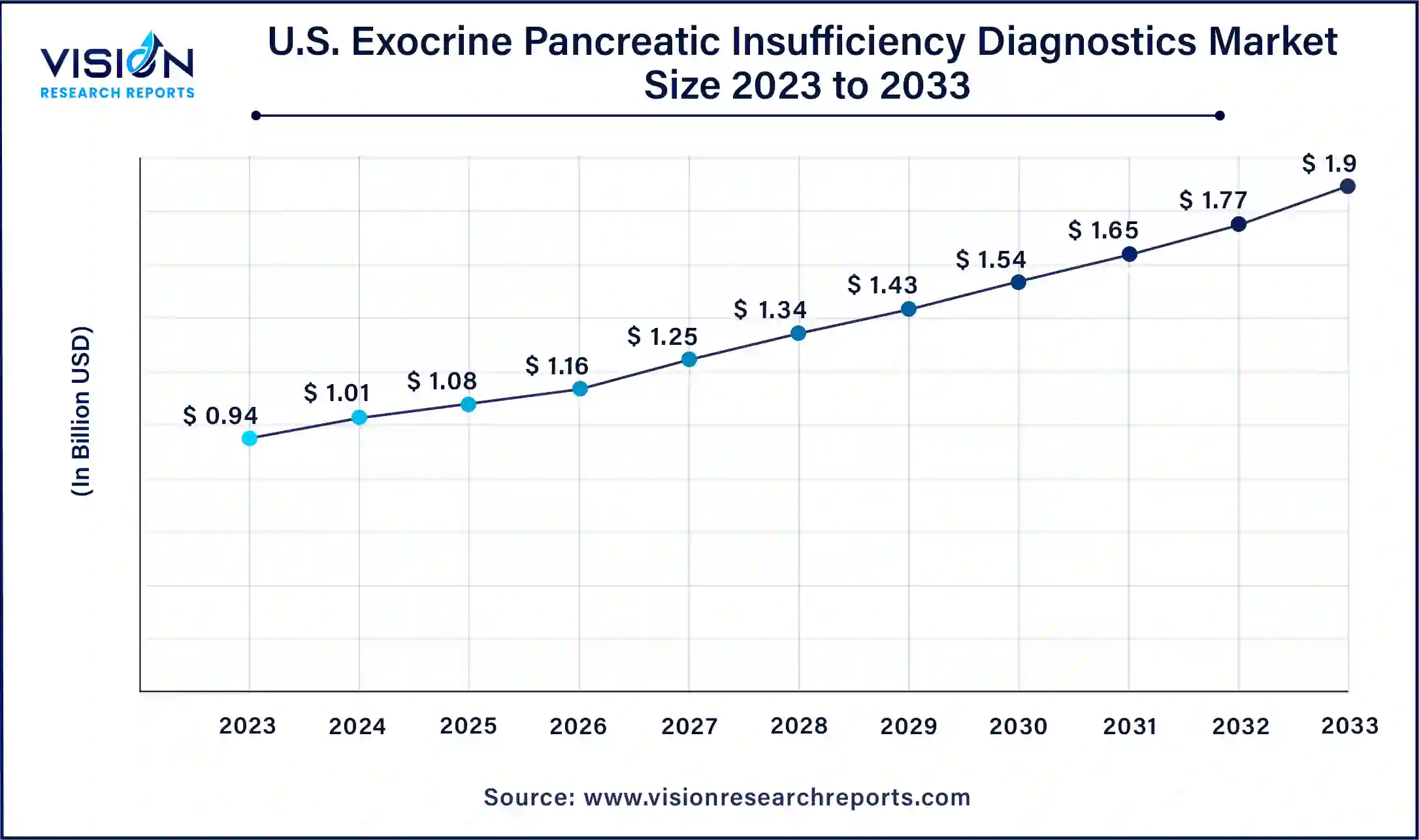
The U.S. exocrine pancreatic insufficiency diagnostics market size was estimated at around USD 0.94 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 1.9 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 7.29% from 2024 to 2033.
The exocrine pancreatic insufficiency diagnostics market in the United States is propelled by the escalating prevalence of target diseases such as chronic pancreatitis, diabetes, pancreatic cancer, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and HIV/AIDS. As the incidence of these conditions continues to rise, there is a corresponding surge in demand for diagnostic tests to accurately identify and manage EPI, thereby driving market growth in the U.S.
North America dominates the exocrine pancreatic insufficiency diagnostics market, capturing the largest revenue share of 48% in 2023. The region's robust healthcare infrastructure, comprising advanced hospitals, clinics, and diagnostic facilities, facilitates widespread access to diagnostic services for EPI. This accessibility encourages greater numbers of individuals to seek testing, thereby driving market demand. Additionally, heightened awareness among healthcare professionals and the general populace about EPI and its associated symptoms has led to increased diagnosis rates. Educational initiatives, medical conferences, and advocacy groups have all contributed to this heightened awareness, resulting in a surge in referrals for diagnostic testing in North America.
In Asia Pacific, the exocrine pancreatic insufficiency diagnostics market is poised to witness the fastest growth over the forecast period. Pancreatic exocrine insufficiency (PEI) affects nearly one-fourth of Indian patients with diabetes, underscoring the substantial burden of pancreatic disorders in the region. Meanwhile, approximately 13.5% of the Japanese population is afflicted with either type 2 diabetes or impaired glucose tolerance. These statistics underscore the escalating prevalence of pancreatic-related conditions in Asia Pacific. Consequently, the market in the region is primed for expansion, driven by the escalating demand for advanced diagnostic solutions to effectively address these conditions.
In 2023, laboratory tests dominated the market with a commanding share of 70% and are projected to exhibit the highest compound annual growth rate (CAGR) throughout the forecast period. Among these tests, stool examinations, notably the fecal elastase test, play a pivotal role in diagnosing Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency (EPI) by detecting inadequate levels of pancreatic enzymes. Additionally, blood tests assessing trypsinogen and chymotrypsin levels can serve as indicative markers for pancreatic insufficiency. The surge in this segment is fueled by several factors, including the escalating prevalence of conditions like chronic pancreatitis, a common precursor to EPI, and the advent of automated and more precise testing methodologies. Furthermore, the burgeoning awareness among healthcare practitioners regarding the criticality of early and precise EPI diagnosis propels the demand for these laboratory-based diagnostic assays.
Within the laboratory tests, the category is further divided into indirect pancreatic function tests and other diagnostic assays. Indirect pancreatic function tests are poised to register the swiftest CAGR over the forecast period. These tests are instrumental in EPI diagnosis as they evaluate the pancreas's capacity to secrete enzymes crucial for digestion. By measuring specific substances like fecal elastase-1 in stool or blood samples, these tests offer insights into pancreatic dysfunction. The growth trajectory of indirect pancreatic function tests is driven by the mounting prevalence of conditions such as chronic pancreatitis and cystic fibrosis, which serve as primary risk factors for EPI.
Hospitals and clinics emerged as the dominant end-use segment, commanding a share of 55% in 2023, and are projected to experience the highest compound annual growth rate (CAGR) during the forecast period. The advancements in diagnostic technologies have revolutionized the landscape of Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency (EPI) detection, significantly enhancing accuracy and efficiency. From traditional methods like fecal elastase tests to more sophisticated imaging techniques such as MRI and CT scans, hospitals and clinics now boast a myriad of options for diagnosing EPI, resulting in increased patient referrals and revenue generation.
The escalating prevalence of EPI, attributed to factors like aging populations, lifestyle modifications, and heightened awareness among healthcare practitioners, has spurred a surge in demand for diagnostic services in hospitals and clinics. This trend is expected to persist as the global incidence of EPI continues to climb. Moreover, the growing emphasis on early detection and intervention for EPI, aimed at averting complications like malnutrition and digestive disorders, has further bolstered the demand for diagnostic tests in these healthcare settings. Healthcare providers increasingly recognize the pivotal role of timely diagnosis in enhancing patient outcomes, thus propelling the growth of this segment.
By Diagnostic Method
By End-use
By Region
 Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
 Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
 Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
 Country/Region-specific Report
Country/Region-specific Report
 Go To Market Strategy
Go To Market Strategy
 Region Specific Market Dynamics
Region Specific Market Dynamics Region Level Market Share
Region Level Market Share Import Export Analysis
Import Export Analysis Production Analysis
Production Analysis Others
Others