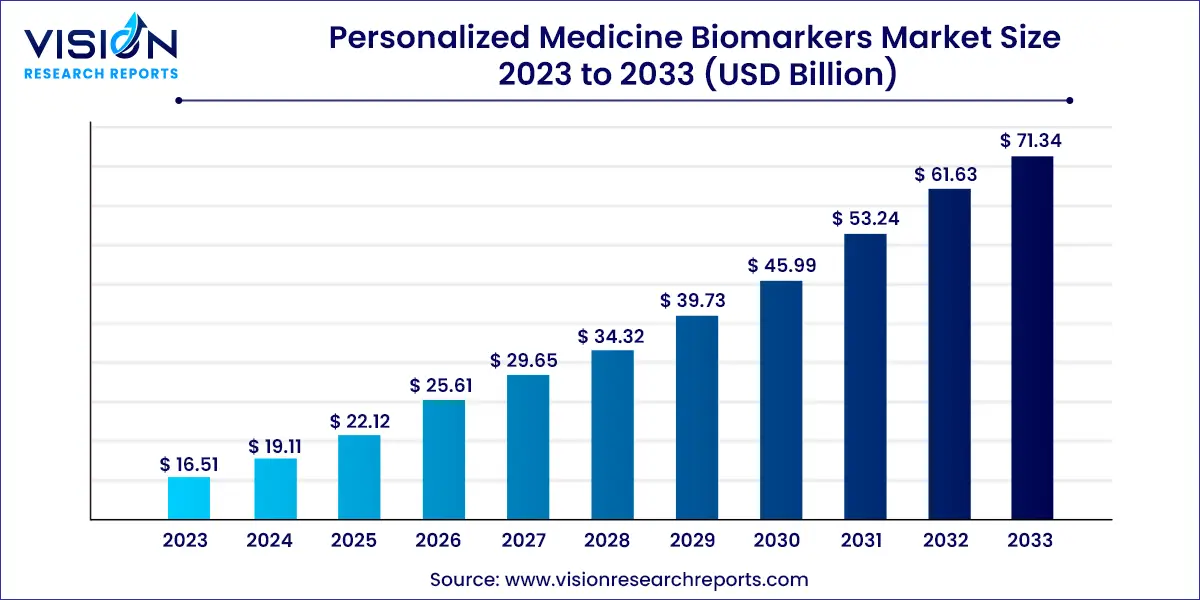
The global personalized medicine biomarkers market size was valued at USD 16.51 billion in 2023 and it is predicted to surpass around USD 71.34 billion by 2033 with a CAGR of 15.76% from 2024 to 2033. The personalized medicine biomarkers market has been experiencing significant growth in recent years. Personalized medicine focuses on tailoring medical treatment to the individual characteristics of each patient. Biomarkers play a crucial role in this process by providing specific information about a patient's health status, disease progression, or response to treatment. Biomarkers are measurable indicators of biological processes or diseases, which can be found in blood, tissue, or other body fluids.
The personalized medicine biomarkers market is poised for significant growth due to the rising prevalence of chronic diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular disorders, and diabetes is driving the demand for more precise and tailored treatment options. Biomarkers enable healthcare providers to diagnose these conditions early, monitor disease progression, and predict patient responses to specific treatments, thereby improving patient outcomes. Second, technological advancements in genomics, proteomics, and bioinformatics have facilitated the identification and validation of new biomarkers, making personalized medicine more accessible and accurate. Additionally, the increasing investment by pharmaceutical companies and research institutions in biomarker discovery and development is accelerating market expansion.
North America is currently the leading region in the market, largely due to the high adoption rate of advanced medical technologies, a strong healthcare infrastructure, and significant investment in personalized medicine research. The United States, in particular, plays a pivotal role, with numerous biotechnology companies, academic institutions, and research organizations actively engaged in the discovery and development of novel biomarkers.
Europe follows closely behind, benefiting from a robust healthcare system and widespread awareness of personalized medicine. Countries such as the United Kingdom, Germany, and France are at the forefront of research efforts, supported by strong collaborations between public health institutions and private companies. The European Union’s focus on precision medicine initiatives and funding for biomarker research also contributes to the growth of the market.
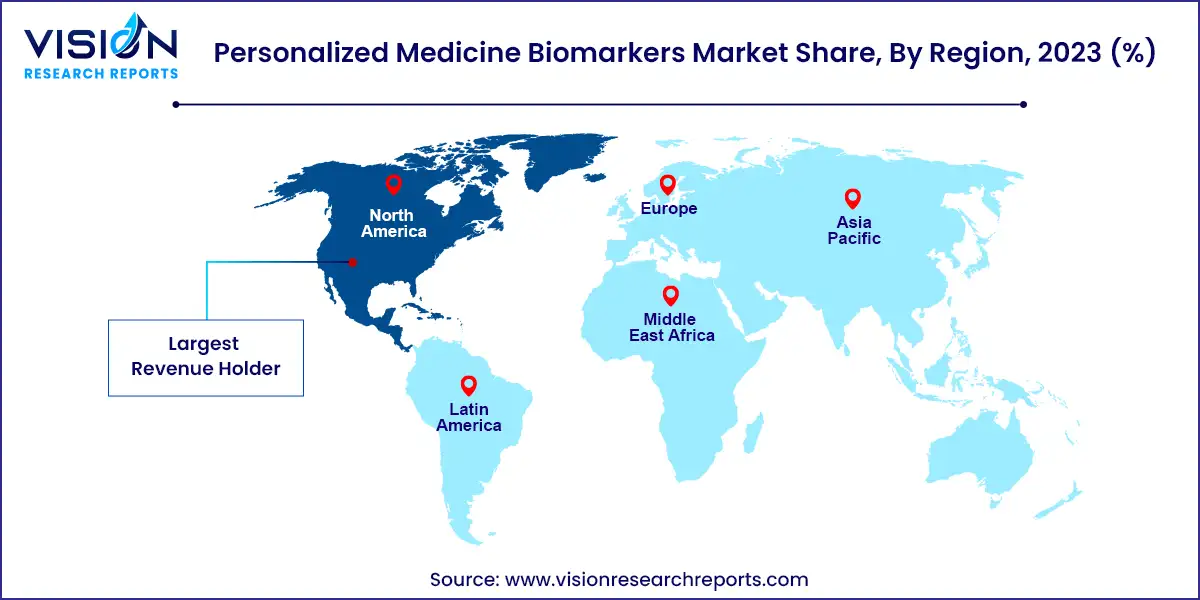
The Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a significant player in the personalized medicine biomarkers market due to its large patient population and increasing prevalence of chronic diseases. Countries like China, Japan, and India are investing heavily in healthcare modernization and personalized medicine research. The rising incidence of cancer and other chronic diseases, coupled with government initiatives to improve healthcare infrastructure, is driving the demand for biomarker-based diagnostics and personalized therapies.
In Latin America and the Middle East & Africa, the personalized medicine biomarkers market is in the nascent stages but shows promising potential. In Latin America, Brazil and Mexico are leading the market due to improvements in healthcare infrastructure and a growing focus on personalized healthcare. Increasing awareness of the benefits of early diagnosis and targeted treatment options is driving demand in these countries. In the Middle East & Africa, market growth is driven by the rising burden of chronic diseases and the increasing adoption of advanced diagnostic technologies. Governments in these regions are beginning to recognize the importance of personalized medicine, leading to increased investment in healthcare and biomarker research.
The application of personalized medicine biomarkers in early detection, screening, and diagnosis represents a critical aspect of modern healthcare. These biomarkers are essential tools that enable healthcare professionals to identify diseases at their earliest stages, often before symptoms become apparent. Early detection is particularly valuable for diseases like cancer, where timely intervention can significantly improve survival rates and treatment outcomes. Personalized biomarkers offer a more precise and individualized approach to detecting diseases, moving beyond traditional diagnostic methods, which may not be sensitive or specific enough to detect early pathological changes.
In screening applications, personalized medicine biomarkers provide a non-invasive and efficient way to assess large populations for the presence of disease markers. This capability is crucial for public health initiatives aimed at controlling and managing the spread of chronic diseases. Biomarkers can be found in various biological fluids, such as blood, urine, or saliva, making it easier to implement routine screenings without the need for invasive procedures. For example, liquid biopsy techniques utilizing circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) allow for the early detection of cancers with minimal discomfort to the patient, enabling ongoing monitoring of disease progression and treatment response.
The use of personalized medicine biomarkers in oncology has revolutionized cancer care by enabling more precise diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of various cancer types. In oncology, biomarkers play a critical role in identifying genetic mutations, proteins, and other molecular changes associated with cancer development. These biomarkers can be used to detect cancer at an early stage, often before symptoms arise, which significantly improves the chances of successful treatment. For instance, specific biomarkers like BRCA1 and BRCA2 are used to assess the risk of breast and ovarian cancers, while HER2 status is critical in determining treatment options for breast cancer patients. Biomarkers also aid in monitoring disease progression and response to therapy, allowing oncologists to tailor treatment plans to individual patients' needs, minimizing adverse effects and enhancing efficacy.
In the field of neurology, the application of personalized medicine biomarkers is increasingly important for the early detection, diagnosis, and management of neurological disorders. Neurological conditions, such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and multiple sclerosis, often have complex and multifactorial etiologies, making diagnosis and treatment challenging. Biomarkers in neurology can help identify individuals at risk of developing these conditions before the onset of clinical symptoms, facilitating early intervention and potentially slowing disease progression. For example, amyloid-beta and tau proteins are biomarkers associated with Alzheimer's disease, helping to identify and monitor the disease's presence and progression. In Parkinson's disease, biomarkers such as alpha-synuclein are being studied to improve early diagnosis and monitor the effectiveness of treatments. The use of biomarkers in neurology also aids in the stratification of patients based on disease subtypes or stages, ensuring that patients receive the most appropriate therapies for their specific condition.
By Application
By Indication
By Region
 Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
 Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
 Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
 Country/Region-specific Report
Country/Region-specific Report
 Go To Market Strategy
Go To Market Strategy
 Region Specific Market Dynamics
Region Specific Market Dynamics Region Level Market Share
Region Level Market Share Import Export Analysis
Import Export Analysis Production Analysis
Production Analysis Others
Others