The global skin cancer diagnostic market size was estimated at around USD 9.16 billion in 2023 and it is projected to hit around USD 15.71 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 5.54% from 2024 to 2033. The global skin cancer diagnostics market has seen substantial growth driven by rising skin cancer prevalence, advances in diagnostic technologies, and increased public awareness.
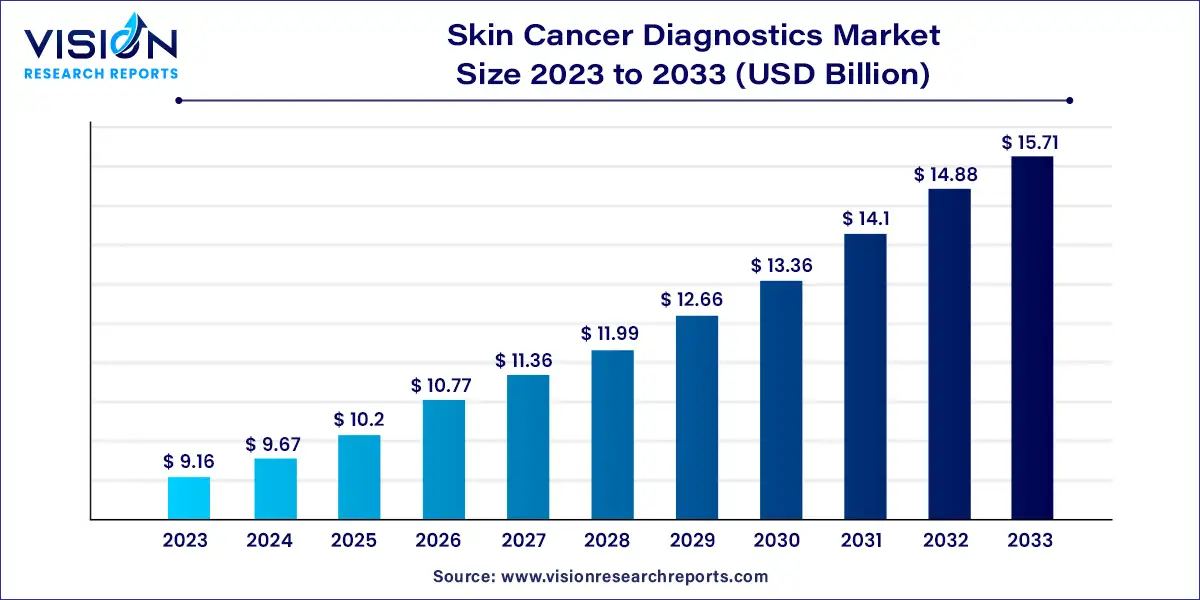
The growth of the skin cancer diagnostics market is propelled by the increasing incidence of skin cancer worldwide, driven by factors such as prolonged UV exposure and aging populations, is significantly boosting the demand for effective diagnostic solutions. Technological advancements in diagnostic tools, including non-invasive imaging techniques and AI-driven diagnostic algorithms, are enhancing early detection and accuracy, thereby expanding the market. Additionally, growing public awareness and educational campaigns about the importance of early skin cancer detection are encouraging more individuals to seek regular screenings. Government initiatives and funding for skin cancer research further support the development and adoption of innovative diagnostic methods.
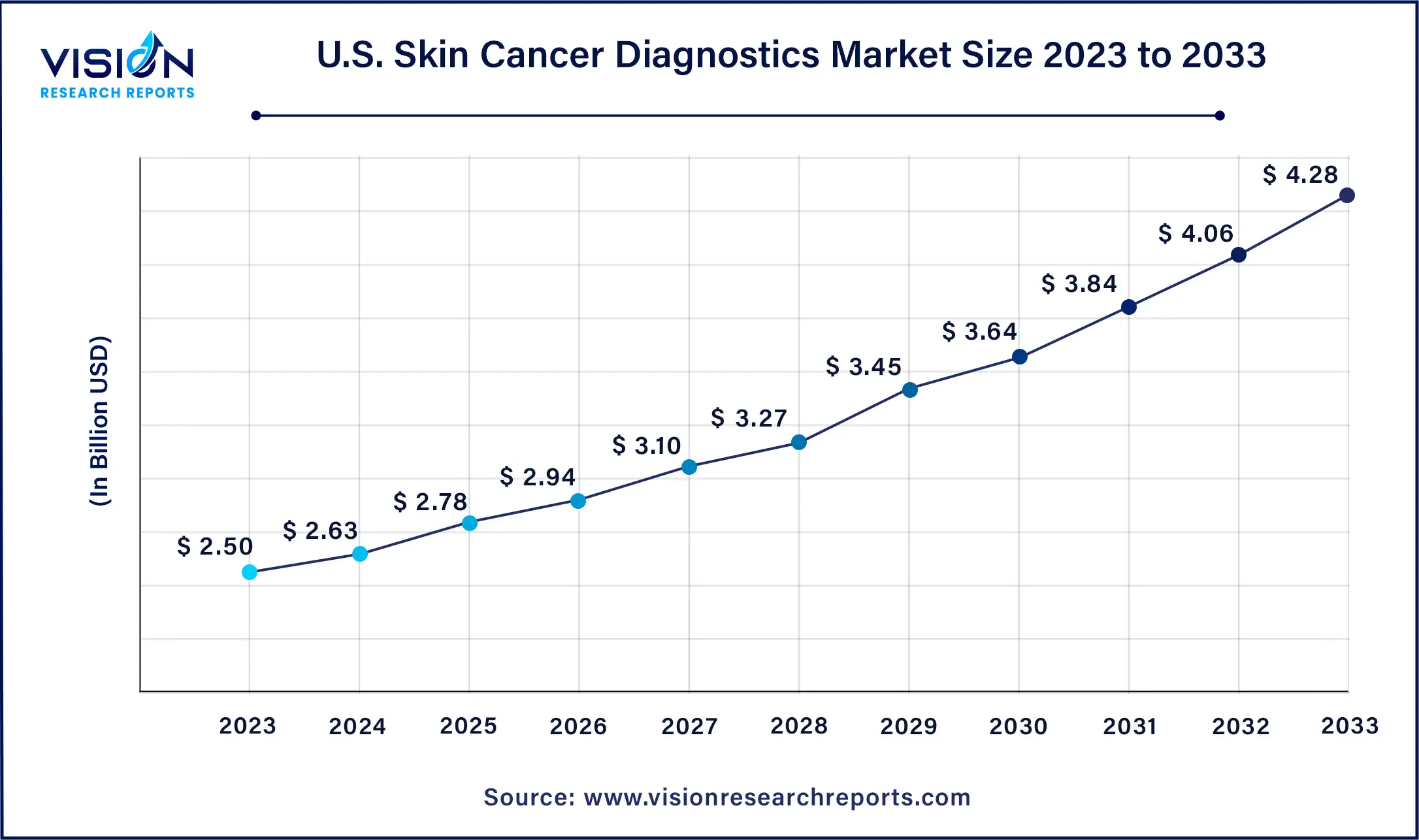
The U.S. skin cancer diagnostic market size was valued at USD 2.50 billion in 2023 and is anticipated to reach around USD 4.28 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 5.52% from 2024 to 2033.
In 2023, the North American skin cancer diagnostics market accounted for a 39% share. Skin cancer is the most prevalent form of cancer in the U.S., with approximately one in five individuals expected to suffer from skin cancer in their lifetime. An estimated 9,500 individuals in the U.S. receive a skin cancer diagnosis daily. NMSC, including BCC and SCC, affects over 3 million U.S. citizens annually. Additionally, strategic initiatives undertaken by key market players offer lucrative opportunities for market growth over the forecast period. In May 2024, Epredia, a subsidiary of PHC Holdings Corporation, partnered with NovaScan, Inc. to sign a letter of intent for an exclusive commercial distribution agreement in the U.S. for MarginScan. This medical device is designed to aid physicians in the real-time detection of NMSC, driving innovation and providing a wide range of products to meet market demand.
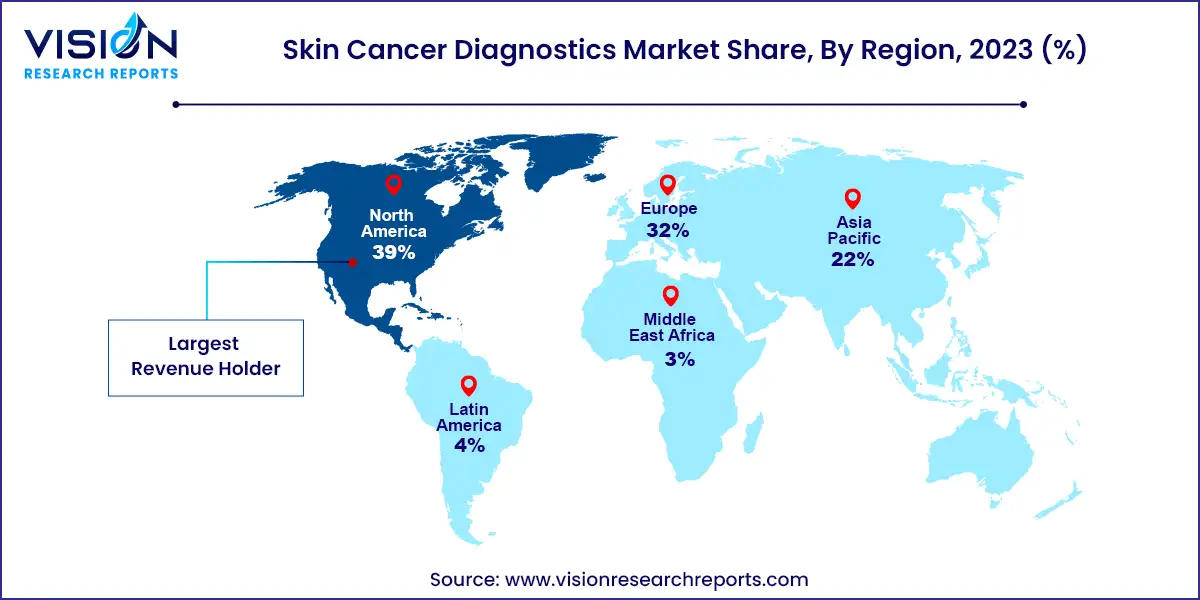
The Asia Pacific is anticipated to witness the fastest growth in the skin cancer diagnostics market, driven by increasing awareness of skin cancer, rising incidences due to environmental factors such as UV exposure, and advancements in diagnostic technologies. Growing healthcare expenditure and improved access to medical facilities also contribute to market growth, along with government initiatives promoting early detection and treatment of skin cancer.
On the basis of cancer type, the nonmelanoma segment held the largest market share of 75% in 2023. The rising incidence of Nonmelanoma Skin Cancer (NMSC) is a significant driver for novel technologies in screening and diagnosis. Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC) and Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC), which make up 70% and 25% of NMSC cases respectively, are the most prevalent forms of skin cancer, accounting for 90% of all malignant skin tumors. Studies predict a continued increase in NMSC cases until at least 2040, underscoring the urgent need for reliable screening tools.
Additionally, deep learning, a form of AI, shows promise in image analysis and is particularly attractive for NMSC diagnosis. As NMSC cases rise globally, there is a growing demand for early detection tools. Deep learning has emerged as a valuable decision-support tool in medicine, offering significant potential in image analysis, a critical aspect of dermatology diagnoses. Dermatology heavily relies on visual diagnoses, making deep learning’s image analysis capabilities highly relevant for diagnosing skin cancer. With the widespread availability of smartphones equipped with powerful cameras, deep learning technology can also be leveraged for remote skin cancer screening. Current data indicates that deep learning technology for detecting and diagnosing cancer offers sensitivity and specificity comparable to trained dermatologists.
In 2023, skin biopsy led the skin cancer diagnostics market with a market share of 32%. Skin biopsy is a fundamental diagnostic procedure in dermatology, with various methods available for different situations. Factors such as lesion type, location, and suspected diagnosis influence the choice of biopsy technique. Histopathologic evaluation remains the gold standard for diagnosing skin cancer, providing crucial information for treatment planning and prognosis.
The imaging tests segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR during the forecast period. Emerging optical imaging modalities, including Reflectance Confocal Microscopy (RCM), Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT), Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), Near-infrared (NIR) bioimaging, and Positron Emission Tomography (PET), offer noninvasive imaging data that can aid in the early detection of cutaneous tumors and assist in surgical planning. These modalities are valuable for observing dynamic processes, such as blood flow, immune cell activation, and tumor energy metabolism, which are relevant for disease progression.
Hospitals and clinics led the skin cancer diagnostics market with a market share of 54% in 2023. Additionally, this segment is expected to be the fastest-growing over the forecast period. Its growth can be attributed to the increasing incidence of skin cancer, advancements in diagnostic technologies, and rising awareness about early detection. The integration of AI and teledermatology in hospitals can further enhance diagnostic accuracy and accessibility, boosting the demand for hospital-based skin cancer diagnostic services.
In May 2023, the UK NHS planned to accelerate the rollout of teledermatology, which involves taking high-resolution images of skin spots, moles, or lesions for faster diagnosis and treatment of skin cancer. This technology uses a small lens attached to a phone camera (dermatoscope), allowing dermatologists to double the number of patients they can review daily. Teledermatology, currently used in about 15% of trusts offering dermatology services, was expected to be available in all areas by July 2023. It would also be expanded to GP practices, aiding people in rural areas and reducing the need for specialist appointments. More than 600,000 people were referred for skin cancer checks last year, a 9% increase from the previous year.
NHS trusts are expanding the use of teledermatology in community diagnostic centers to reduce waiting times. Patients can be referred directly to a local diagnostic hub, avoiding the need for a face-to-face appointment. Additionally, magnifying lenses using AI technology are being trialed to assess lesions quickly and accurately. This technology has helped avoid around 10,000 unnecessary face-to-face appointments. Moreover, it has enabled some hospitals to diagnose and treat virtually all skin cancer patients within 2 months of GP referral. The NHS's focus on technology-driven advancements in cancer diagnosis and treatment is expected to significantly improve patient outcomes and reduce the burden on healthcare resources.
By Cancer Type
By Test Type
By End-use
By Region
 Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
 Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
 Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
 Country/Region-specific Report
Country/Region-specific Report
 Go To Market Strategy
Go To Market Strategy
 Region Specific Market Dynamics
Region Specific Market Dynamics Region Level Market Share
Region Level Market Share Import Export Analysis
Import Export Analysis Production Analysis
Production Analysis Others
Others