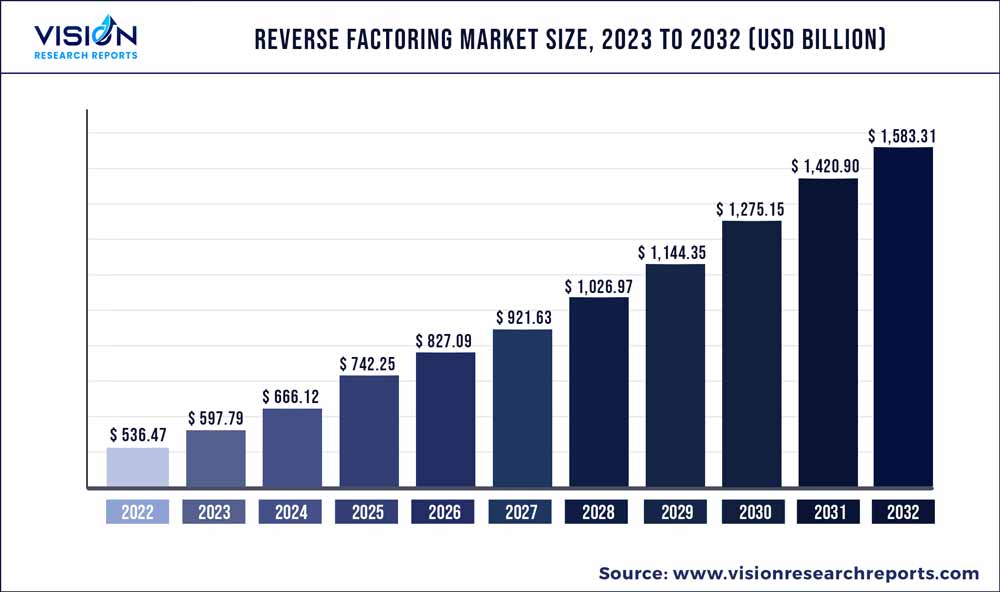
The global reverse factoring market was surpassed at USD 536.47 billion in 2022 and is expected to hit around USD 1,583.31 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 11.43% from 2023 to 2032. The reverse factoring market in the United States was accounted for USD 11.7 billion in 2022.
Key Players
Report Scope of the Reverse Factoring Market
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Revenue Share of Europe in 2022 | 60.16% |
| CAGR of Latin America from 2023 to 2032 | 18.04% |
| Revenue Forecast by 2032 | USD 1,583.31 billion |
| Growth Rate from 2023 to 2032 | CAGR of 11.43% |
| Base Year | 2022 |
| Forecast Period | 2023 to 2032 |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Companies Covered | Accion International; Banco Bilbao Vizcaya Argentaria, S.A.; Barclays Plc; Credit Suisse Group AG; Deutsche Factoring Bank; Drip Capital Inc.; eFactor Network; HSBC Group; JP Morgan Chase & Co.; Mitsubishi UFJ Financial Group, Inc.; PrimeRevenue, Inc.; Societe Generale; Trade Finance Global; TRADEWIND GMBH; Viva Capital Funding, LLC |
The reverse factoring or supply chain financing (SCF) market’s growth can be attributed to the growing need for alternative financing solutions in Micro, Small & Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) to improve their cash flow.
Further, reverse factoring, or SCF, offers various benefits, such as developing long-term relationships between suppliers & buyers, improved balance sheet efficiency, and smoother cash flow, supporting the growth of the supply chain financing market. The COVID-19 pandemic affected the overall reverse factoring industry due to disruptions in business operations and supply chains. However, from early 2021 with ease in lockdown, the end-use companies preferred reverse factoring into their business models to accelerate product development and production and gain a competitive edge over their rivals.
The MEMSs are facing various challenges in raising their working capital owing to the limited availability of adequate financing solutions. To overcome this challenge, MSMEs have shifted their focus towards factoring and reverse factoring solutions to streamline their cash flows, which is anticipated to support the reverse factoring industry’s growth globally. Various countries' governments, such as India, Canada, and Japan, are taking supportive initiatives to assist MSMSs in raising working capital and supporting market growth.
For instance, in January 2021, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) allowed non-deposit-taking NBFC and Investment Credit Companies (ICCs) with assets of around USD 130 million and above to provide various factoring services, including SCF and bill discount facilities to MSMEs. It helped MSMEs get immediate liquidity instead of waiting for bills to be honored by customers.
The increasing demand for reverse factoring solutions globally is encouraging market players to adopt various business opportunities, supporting the growth of the industry. For instance, in December 2022, eFactor Network and Trafigura Pte. Ltd., a company operating in the commodities industry, announced that they are collaborating with several financial institutions and piloting a Sustainable Supply Chain Finance program for mining companies based in Mexico.
The program envisaged strengthening mining companies' working capital while encouraging responsible sourcing practices throughout the value chain. The program particularly envisaged leveraging eFactor Network's digital factoring platform to provide Trafigura Pte. Ltd.'s suppliers of metal concentrates with accelerated payments for products.
Category Insights
The domestic segment accounted for the largest market share of 92.74% in 2022. The segment growth can be attributed to the increasing adoption of SCF services among domestic MSMEs due to its effectiveness. Most of the suppliers across the globe are Micro, Small & Medium-sized Enterprises (MSMEs). Delayed payments from the buyers make it difficult for suppliers to ensure consistent production cycles.
The issue is further aggravated as the suppliers have no alternate finance access, affecting their overall business operations. To overcome these issues, MSMEs are now adopting reverse factoring to optimize their inventory stock and prevent business loss due to finance scarcity.
The international segment is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 14.45% during the forecast period. The international segment is expected to witness significant growth owing to the rising demand for open trade accounts, especially from suppliers in emerging countries. International reverse factoring services are a requisite for organizations engaging in international trade, irrespective of their current industry and size.
Apart from lowering the credit risk, international reverse factoring offers numerous other benefits, such as easy availability of information on current and prospective clients, expansion into foreign markets, less documentation, improved working capital, overcoming issues related to foreign customs, supporting the growth of the international reverse factoring industry.
Financial Institution Insights
The bank segment accounted for a market share of 81.81% in 2022. The growth can be attributed to the rising popularity of digitalization to fill the current gaps in various financial services and shifting various banks' focus on offering enhanced consumer experience.
Increasing cross-border transactions and significant adoption of mobile-based payment systems is expected to propel the growth of the bank segment over the forecast period. Moreover, the growing use of Blockchain technology by banks to address constraints in raising working capital and cash flows is boosting the proliferation of reverse factoring services in banks.
The Non-Banking Financial Institutions (NBFIs) segment is expected to grow at the highest CAGR of 13.06% during the forecast period. The NBFIs offers improved transparency & flexibility in their reverse factoring solutions and helps various businesses in dealing with evolving supply chain and geopolitical environment, creating robust opportunities for the reverse factoring industry.
NBFIs provide trade expertise with the use of digital solutions to improve the trade of their domestic and international clients. Furthermore, NBFIs are adopting emerging technologies such as AI, ML, and data analytics to overcome various challenges in credit & deposit systems, asset management, & lending and provide several services, including alternative credit model and regulatory compliance, supporting segment growth in the supply chain financing market.
End-use Insights
The manufacturing segment accounted for the largest market share of 30.72% in 2022. Reverse factoring improves cash flow by providing suppliers with the option of receiving early invoice payments and extending a manufacturer's supplier payment terms. Reverse factoring services are used by manufacturing companies across various sectors, such as chemical, metal & machinery, welding, pallet, and plastics & polymers, creating a positive market outlook for supply chain financing services.
Furthermore, reverse factoring allows manufacturing companies to keep multiple relations with banks and an opportunity to provide liquidity. Moreover, it also enables manufacturing companies a better visibility in invoice status and payment processing which allows them to know the payment date, which mitigates the risk of disrupting the relationship with the supplier, creating a positive outlook for the supply chain financing market.
The healthcare segment is expected to grow at the highest CAGR of 13.94% during the forecast period. Manufacturers in the healthcare sector are taking various initiatives to expand their business operations. However, these initiatives are expensive and require frequent funding. When healthcare companies face issues in business expansion, reverse factoring can help them bring desired changes to the business models and expand their business operations.
Furthermore, reverse factoring also helps to improve the company’s cash position. The improved cash position encourages the company to invest in R&D operations to enhance its product portfolio and market position, creating a favorable environment for the reverse factoring industry in the healthcare sector.
Regional Insights
Europe held a significant share of 60.16% of the target market in 2022. The significant growth of the Europe reverse factoring market can be attributed to increasing business activity levels, availability of quick expert advice for financial management from a majority of the firms, and significant penetration of the market leaders in the region. Supportive government initiatives to assist start-ups in raising public & private funding and focus on established reverse factoring service providers on offering alternative financial assistance by buying SMEs’ pending invoices are creating a positive market outlook in Europe.
Latin America is anticipated to grow as the fastest-developing regional market at a CAGR of 18.04% through 2032. The growth of Latin America's reverse factoring industry can be attributed to the shift in focus of companies from various sectors on bad debt evasion and business growth with better financial stability. Several Latin American countries, such as Argentina, Peru, Chile, Mexico, and Brazil, are witnessing rising demand for reverse factoring services in most sectors.
Furthermore, domestic and international factoring services are used to offer exporters easy access to funds by transforming discounted receivables of the company into improved cash flows. Increasing F&B industry and staffing agencies penetration in the region is creating a positive market outlook for multiple financing solutions, creating robust opportunities for the reverse factoring industry.
Reverse Factoring Market Segmentations:
By Category
By Financial Institution
By End-use
By Regional
Chapter 1. Introduction
1.1. Research Objective
1.2. Scope of the Study
1.3. Definition
Chapter 2. Research Methodology
2.1. Research Approach
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Assumptions & Limitations
Chapter 3. Executive Summary
3.1. Market Snapshot
Chapter 4. Market Variables and Scope
4.1. Introduction
4.2. Market Classification and Scope
4.3. Industry Value Chain Analysis
4.3.1. Raw Material Procurement Analysis
4.3.2. Sales and Distribution Category Analysis
4.3.3. Downstream Buyer Analysis
Chapter 5. COVID 19 Impact on Reverse Factoring Market
5.1. COVID-19 Landscape: Reverse Factoring Industry Impact
5.2. COVID 19 - Impact Assessment for the Industry
5.3. COVID 19 Impact: Global Major Government Policy
5.4. Market Trends and Opportunities in the COVID-19 Landscape
Chapter 6. Market Dynamics Analysis and Trends
6.1. Market Dynamics
6.1.1. Market Drivers
6.1.2. Market Restraints
6.1.3. Market Opportunities
6.2. Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
6.2.1. Bargaining power of suppliers
6.2.2. Bargaining power of buyers
6.2.3. Threat of substitute
6.2.4. Threat of new entrants
6.2.5. Degree of competition
Chapter 7. Competitive Landscape
7.1.1. Company Market Share/Positioning Analysis
7.1.2. Key Strategies Adopted by Players
7.1.3. Vendor Landscape
7.1.3.1. List of Suppliers
7.1.3.2. List of Buyers
Chapter 8. Global Reverse Factoring Market, By Category
8.1. Reverse Factoring Market, by Category, 2023-2032
8.1.1 Domestic
8.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2020-2032)
8.1.2. International
8.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2020-2032)
Chapter 9. Global Reverse Factoring Market, By Financial Institution
9.1. Reverse Factoring Market, by Financial Institution, 2023-2032
9.1.1. Banks
9.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2020-2032)
9.1.2. Non-banking Financial Institutions
9.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2020-2032)
Chapter 10. Global Reverse Factoring Market, By End-use
10.1. Reverse Factoring Market, by End-use, 2023-2032
10.1.1. Manufacturing
10.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2020-2032)
10.1.2. Transport & Logistics
10.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2020-2032)
10.1.3. Information Technology
10.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2020-2032)
10.1.4. Healthcare
10.1.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2020-2032)
10.1.5. Construction
10.1.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2020-2032)
10.1.6. Others (Retail, Food & Beverages, Among Others)
10.1.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2020-2032)
Chapter 11. Global Reverse Factoring Market, Regional Estimates and Trend Forecast
11.1. North America
11.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Category (2020-2032)
11.1.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Financial Institution (2020-2032)
11.1.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use (2020-2032)
11.1.4. U.S.
11.1.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Category (2020-2032)
11.1.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Financial Institution (2020-2032)
11.1.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use (2020-2032)
11.1.5. Rest of North America
11.1.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Category (2020-2032)
11.1.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Financial Institution (2020-2032)
11.1.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use (2020-2032)
11.2. Europe
11.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Category (2020-2032)
11.2.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Financial Institution (2020-2032)
11.2.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use (2020-2032)
11.2.4. UK
11.2.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Category (2020-2032)
11.2.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Financial Institution (2020-2032)
11.2.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use (2020-2032)
11.2.5. Germany
11.2.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Category (2020-2032)
11.2.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Financial Institution (2020-2032)
11.2.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use (2020-2032)
11.2.6. France
11.2.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Category (2020-2032)
11.2.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Financial Institution (2020-2032)
11.2.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use (2020-2032)
11.2.7. Rest of Europe
11.2.7.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Category (2020-2032)
11.2.7.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Financial Institution (2020-2032)
11.2.7.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use (2020-2032)
11.3. APAC
11.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Category (2020-2032)
11.3.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Financial Institution (2020-2032)
11.3.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use (2020-2032)
11.3.4. India
11.3.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Category (2020-2032)
11.3.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Financial Institution (2020-2032)
11.3.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use (2020-2032)
11.3.5. China
11.3.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Category (2020-2032)
11.3.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Financial Institution (2020-2032)
11.3.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use (2020-2032)
11.3.6. Japan
11.3.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Category (2020-2032)
11.3.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Financial Institution (2020-2032)
11.3.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use (2020-2032)
11.3.7. Rest of APAC
11.3.7.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Category (2020-2032)
11.3.7.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Financial Institution (2020-2032)
11.3.7.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use (2020-2032)
11.4. MEA
11.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Category (2020-2032)
11.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Financial Institution (2020-2032)
11.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use (2020-2032)
11.4.4. GCC
11.4.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Category (2020-2032)
11.4.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Financial Institution (2020-2032)
11.4.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use (2020-2032)
11.4.5. North Africa
11.4.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Category (2020-2032)
11.4.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Financial Institution (2020-2032)
11.4.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use (2020-2032)
11.4.6. South Africa
11.4.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Category (2020-2032)
11.4.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Financial Institution (2020-2032)
11.4.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use (2020-2032)
11.4.7. Rest of MEA
11.4.7.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Category (2020-2032)
11.4.7.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Financial Institution (2020-2032)
11.4.7.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use (2020-2032)
11.5. Latin America
11.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Category (2020-2032)
11.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Financial Institution (2020-2032)
11.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use (2020-2032)
11.5.4. Brazil
11.5.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Category (2020-2032)
11.5.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Financial Institution (2020-2032)
11.5.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use (2020-2032)
11.5.5. Rest of LATAM
11.5.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Category (2020-2032)
11.5.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Financial Institution (2020-2032)
11.5.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use (2020-2032)
Chapter 12. Company Profiles
12.1. Accion International
12.1.1. Company Overview
12.1.2. Product Offerings
12.1.3. Financial Performance
12.1.4. Recent Initiatives
12.2. Banco Bilbao Vizcaya Argentaria, S.A.
12.2.1. Company Overview
12.2.2. Product Offerings
12.2.3. Financial Performance
12.2.4. Recent Initiatives
12.3. Barclays Plc
12.3.1. Company Overview
12.3.2. Product Offerings
12.3.3. Financial Performance
12.3.4. Recent Initiatives
12.4. Credit Suisse Group AG
12.4.1. Company Overview
12.4.2. Product Offerings
12.4.3. Financial Performance
12.4.4. Recent Initiatives
12.5. Deutsche Factoring Bank
12.5.1. Company Overview
12.5.2. Product Offerings
12.5.3. Financial Performance
12.5.4. Recent Initiatives
12.6. Drip Capital Inc.
12.6.1. Company Overview
12.6.2. Product Offerings
12.6.3. Financial Performance
12.6.4. Recent Initiatives
12.7. eFactor Network
12.7.1. Company Overview
12.7.2. Product Offerings
12.7.3. Financial Performance
12.7.4. Recent Initiatives
12.8. HSBC Group
12.8.1. Company Overview
12.8.2. Product Offerings
12.8.3. Financial Performance
12.8.4. Recent Initiatives
12.9. JP Morgan Chase & Co.
12.9.1. Company Overview
12.9.2. Product Offerings
12.9.3. Financial Performance
12.9.4. Recent Initiatives
12.10. Mitsubishi UFJ Financial Group, Inc.
12.10.1. Company Overview
12.10.2. Product Offerings
12.10.3. Financial Performance
12.10.4. Recent Initiatives
Chapter 13. Research Methodology
13.1. Primary Research
13.2. Secondary Research
13.3. Assumptions
Chapter 14. Appendix
14.1. About Us
14.2. Glossary of Terms
 Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
 Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
 Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
 Country/Region-specific Report
Country/Region-specific Report
 Go To Market Strategy
Go To Market Strategy
 Region Specific Market Dynamics
Region Specific Market Dynamics Region Level Market Share
Region Level Market Share Import Export Analysis
Import Export Analysis Production Analysis
Production Analysis Others
Others