The global generic drugs market was estimated at USD 464.97 billion in 2023 and it is expected to surpass around USD 775.61 billion by 2033, poised to grow at a CAGR of 5.25% from 2024 to 2033.
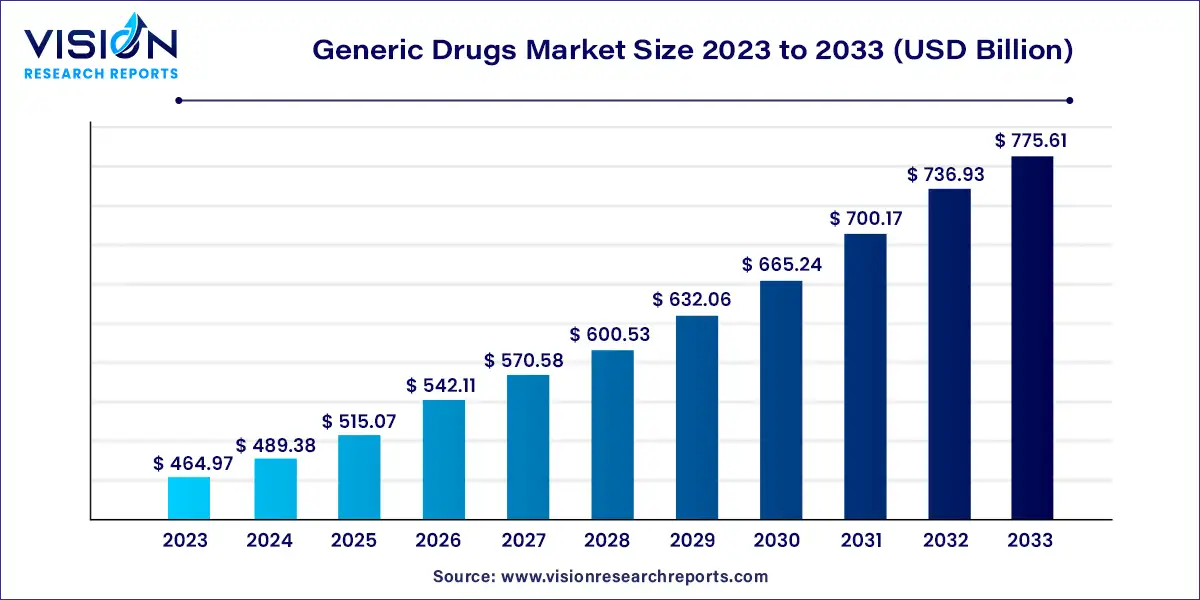
The generic drugs market plays a pivotal role in expanding access to essential medications worldwide by offering cost-effective alternatives to branded drugs. As a result, it contributes significantly to healthcare affordability and accessibility, particularly in emerging economies.
The growth of the generic drugs market is propelled by the patent expirations of branded medications create opportunities for generic manufacturers to introduce equivalent versions at lower costs, driving market expansion. Secondly, the increasing demand for affordable healthcare solutions, particularly in emerging economies, fuels the adoption of generic drugs. Additionally, regulatory initiatives aimed at promoting generic drug usage, such as generic substitution policies and expedited approval processes, contribute to market growth. Moreover, the aging population worldwide drives the demand for pharmaceuticals, including generic medications, to manage chronic conditions and age-related illnesses.
The pure generics segment accounted largest revenue share 53% in 2023. Pure generic drugs, also known as unbranded or off-patent generics, are manufactured and sold under their chemical name without any branding or proprietary identification. These medications are bioequivalent to their branded counterparts, containing the same active ingredients, dosage form, strength, route of administration, and intended use. Pure generic drugs offer significant cost savings compared to branded medications, making them an attractive choice for healthcare providers, insurers, and patients seeking more affordable treatment options without compromising on quality or efficacy.
On the other hand, branded generic drugs are generic medications marketed under a brand name by a pharmaceutical company. Unlike pure generics, branded generics may have their own unique brand name, packaging, and marketing strategies, distinguishing them from other generic counterparts. Branded generic drugs are often introduced to the market by pharmaceutical companies looking to leverage brand recognition, reputation, and marketing efforts to capture market share and differentiate their products from competitors. While branded generics may command slightly higher prices than pure generics due to branding and marketing expenses, they still offer cost savings compared to branded medications and contribute to increased access to affordable healthcare options.
Oral formulations account for around 66% of the global market share in 2023. Oral administration involves the ingestion of medications through the mouth, where the drug is absorbed through the gastrointestinal tract and enters the bloodstream to exert its therapeutic effects. This route of administration is widely utilized due to its convenience, ease of administration, and patient preference. Many generic drugs, including tablets, capsules, and liquids, are formulated for oral administration, offering patients a convenient and non-invasive option for medication delivery. Oral medications are commonly used for a wide range of medical conditions, including chronic diseases, acute illnesses, and preventive healthcare, making them a cornerstone of pharmaceutical therapy worldwide.
In contrast, injection administration involves the delivery of medications directly into the body through the use of needles and syringes, bypassing the gastrointestinal tract for rapid absorption and distribution throughout the body. Injectable medications can be administered via various routes, including intramuscular (into muscle), subcutaneous (under the skin), intravenous (into a vein), and intradermal (into the skin), depending on the specific drug and therapeutic indication. While injection administration may be associated with discomfort and inconvenience compared to oral medications, it offers several advantages, including faster onset of action, higher bioavailability, and greater precision in dosing.
Simple generics, also known as traditional generics, are pharmaceutical products that contain the same active ingredients, dosage form, strength, and route of administration as their branded counterparts. These medications undergo rigorous testing to demonstrate bioequivalence to the original branded drug, ensuring that they are therapeutically equivalent and interchangeable with the reference product. Simple generics are typically introduced to the market after the expiration of patents held by the brand-name manufacturer, allowing generic drug manufacturers to produce and distribute affordable alternatives to branded medications.
In contrast, super generics represent a more advanced category of generic drugs that offer additional benefits beyond traditional generics. Super generics are formulated to enhance drug delivery, efficacy, safety, or patient adherence through innovative technologies or modifications to the drug's formulation. These enhancements may include improved bioavailability, optimized pharmacokinetics, modified release profiles, or novel drug delivery systems, such as nanotechnology or lipid-based formulations. By leveraging advanced pharmaceutical technologies, super generics aim to overcome limitations associated with the original branded drug or traditional generic formulations, offering patients enhanced therapeutic outcomes and improved treatment experiences.
In the expansive landscape of the global generic drugs market, therapeutic applications cover a broad spectrum of medical specialties, with two prominent areas being Central Nervous System (CNS) and Oncology. Within the CNS category, generic drugs play a crucial role in the treatment of various neurological and psychiatric disorders, including depression, anxiety, schizophrenia, epilepsy, and Parkinson's disease, among others. These conditions often require long-term pharmacotherapy to manage symptoms and improve patient outcomes. Generic medications targeting the CNS are formulated to modulate neurotransmitter activity, restore chemical balance in the brain, and alleviate symptoms associated with CNS disorders. By offering affordable alternatives to branded CNS medications, generic drugs enhance access to essential treatments for millions of patients worldwide, reducing healthcare costs and improving treatment adherence.
The oncology segment is observed to witness the fastest rate of expansion at a CAGR of 6.65% during the forecast period. Oncology is another vital therapeutic area within the global generic drugs market, encompassing the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of cancer. Generic oncology drugs include chemotherapeutic agents, targeted therapies, supportive care medications, and hormone therapies used in the management of various cancer types, such as breast, lung, colorectal, prostate, and leukemia, among others. These medications play a pivotal role in cancer treatment regimens, either as standalone therapies or in combination with surgery, radiation, or other modalities. Generic oncology drugs offer significant cost savings compared to their branded counterparts, making cancer treatment more affordable and accessible to patients facing the financial burden of cancer care.
In the expansive landscape of the global generic drugs market, distribution channels play a pivotal role in ensuring widespread accessibility and availability of medications to patients. Two primary distribution channels for generic drugs are retail pharmacy and hospital pharmacy, each serving distinct roles in delivering pharmaceutical products to consumers. Retail pharmacies, commonly found in community settings such as standalone stores, supermarkets, and online platforms, serve as the primary point of contact for patients seeking prescription and over-the-counter medications. These pharmacies stock a wide range of generic drugs alongside branded medications, offering patients the convenience of obtaining their prescriptions close to home or via convenient online ordering platforms.
Hospital pharmacies, on the other hand, operate within healthcare institutions such as hospitals, clinics, and outpatient facilities, providing medications to inpatients and outpatients under the supervision of healthcare professionals. Hospital pharmacies play a critical role in managing medication distribution, ensuring the safe and efficient delivery of medications to patients within the hospital setting. In addition to dispensing medications prescribed by healthcare providers, hospital pharmacies may also engage in compounding, drug preparation, medication reconciliation, and clinical pharmacy services to support patient care and safety.
In 2023, North America secured the largest share of revenue, accounting for 35%. The United States notably recorded the highest sales in the Generic Drugs Market in 2021. Despite the ongoing focus on the pandemic, which has entered its third year with significant disruptions and a death toll nearing 1 million, other crucial dynamics are emerging within the region's healthcare landscape. These include patterns in healthcare service utilization, associated spending levels (including out-of-pocket costs for patients), and the utilization of prescription medications. Understanding these aspects of the healthcare system and their potential evolution in the coming years remains essential for stakeholders and decision-makers, including patients. The spending patterns and growth drivers underscore significant variations in spending levels among stakeholders, with rebates and discounts impacting these trends.
By Drug Type
By Brand
By Route of Drug Administration
By Therapeutic Application
By Distribution Channel
By Region
Chapter 1. Introduction
1.1. Research Objective
1.2. Scope of the Study
1.3. Definition
Chapter 2. Research Methodology
2.1. Research Approach
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Assumptions & Limitations
Chapter 3. Executive Summary
3.1. Market Snapshot
Chapter 4. Market Variables and Scope
4.1. Introduction
4.2. Market Classification and Scope
4.3. Industry Value Chain Analysis
4.3.1. Raw Material Procurement Analysis
4.3.2. Sales and Distribution Channel Analysis
4.3.3. Downstream Buyer Analysis
Chapter 5. COVID 19 Impact on Generic Drugs Market
5.1. COVID-19 Landscape: Generic Drugs Industry Impact
5.2. COVID 19 - Impact Assessment for the Industry
5.3. COVID 19 Impact: Global Major Government Policy
5.4. Market Trends and Opportunities in the COVID-19 Landscape
Chapter 6. Market Dynamics Analysis and Trends
6.1. Market Dynamics
6.1.1. Market Drivers
6.1.2. Market Restraints
6.1.3. Market Opportunities
6.2. Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
6.2.1. Bargaining power of suppliers
6.2.2. Bargaining power of buyers
6.2.3. Threat of substitute
6.2.4. Threat of new entrants
6.2.5. Degree of competition
Chapter 7. Competitive Landscape
7.1.1. Company Market Share/Positioning Analysis
7.1.2. Key Strategies Adopted by Players
7.1.3. Vendor Landscape
7.1.3.1. List of Suppliers
7.1.3.2. List of Buyers
Chapter 8. Global Generic Drugs Market, By Drug Type
8.1. Generic Drugs Market, by Drug Type, 2024-2033
8.1.1. Simple Generics
8.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
8.1.2. Super Generics
8.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
Chapter 9. Global Generic Drugs Market, By Brand
9.1. Generic Drugs Market, by Brand, 2024-2033
9.1.1. Pure generic drugs
9.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
9.1.2. Branded generic drugs
9.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
Chapter 10. Global Generic Drugs Market, By Route of Drug Administration
10.1. Generic Drugs Market, by Route of Drug Administration, 2024-2033
10.1.1. Oral
10.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
10.1.2. Injection
10.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
10.1.3. Cutaneous
10.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
10.1.4. Others
10.1.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
Chapter 11. Global Generic Drugs Market, By Therapeutic Application
11.1. Generic Drugs Market, by Therapeutic Application, 2024-2033
11.1.1. Central Nervous System (CNS)
11.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
11.1.2. Cardiovascular
11.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
11.1.3. Infectious Diseases
11.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
11.1.4. Musculoskeletal Diseases
11.1.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
11.1.5. Respiratory
11.1.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
11.1.6. Oncology
11.1.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
11.1.7. Others
11.1.7.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
Chapter 12. Global Generic Drugs Market, By Distribution Channel
12.1. Generic Drugs Market, by Distribution Channel, 2024-2033
12.1.1. Retail Pharmacy
12.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
12.1.2. Hospital Pharmacy
12.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
12.1.3. Online and Others
12.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
Chapter 13. Global Generic Drugs Market, Regional Estimates and Trend Forecast
13.1. North America
13.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Drug Type (2021-2033)
13.1.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Brand (2021-2033)
13.1.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Route of Drug Administration (2021-2033)
13.1.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Therapeutic Application (2021-2033)
13.1.5. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel (2021-2033)
13.1.6. U.S.
13.1.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Drug Type (2021-2033)
13.1.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Brand (2021-2033)
13.1.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Route of Drug Administration (2021-2033)
13.1.6.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Therapeutic Application (2021-2033)
13.1.7. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel (2021-2033)
13.1.8. Rest of North America
13.1.8.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Drug Type (2021-2033)
13.1.8.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Brand (2021-2033)
13.1.8.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Route of Drug Administration (2021-2033)
13.1.8.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Therapeutic Application (2021-2033)
13.1.8.5. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel (2021-2033)
13.2. Europe
13.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Drug Type (2021-2033)
13.2.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Brand (2021-2033)
13.2.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Route of Drug Administration (2021-2033)
13.2.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Therapeutic Application (2021-2033)
13.2.5. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel (2021-2033)
13.2.6. UK
13.2.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Drug Type (2021-2033)
13.2.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Brand (2021-2033)
13.2.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Route of Drug Administration (2021-2033)
13.2.7. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Therapeutic Application (2021-2033)
13.2.8. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel (2021-2033)
13.2.9. Germany
13.2.9.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Drug Type (2021-2033)
13.2.9.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Brand (2021-2033)
13.2.9.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Route of Drug Administration (2021-2033)
13.2.10. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Therapeutic Application (2021-2033)
13.2.11. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel (2021-2033)
13.2.12. France
13.2.12.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Drug Type (2021-2033)
13.2.12.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Brand (2021-2033)
13.2.12.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Route of Drug Administration (2021-2033)
13.2.12.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Therapeutic Application (2021-2033)
13.2.13. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel (2021-2033)
13.2.14. Rest of Europe
13.2.14.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Drug Type (2021-2033)
13.2.14.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Brand (2021-2033)
13.2.14.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Route of Drug Administration (2021-2033)
13.2.14.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Therapeutic Application (2021-2033)
13.2.15. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel (2021-2033)
13.3. APAC
13.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Drug Type (2021-2033)
13.3.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Brand (2021-2033)
13.3.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Route of Drug Administration (2021-2033)
13.3.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Therapeutic Application (2021-2033)
13.3.5. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel (2021-2033)
13.3.6. India
13.3.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Drug Type (2021-2033)
13.3.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Brand (2021-2033)
13.3.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Route of Drug Administration (2021-2033)
13.3.6.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Therapeutic Application (2021-2033)
13.3.7. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel (2021-2033)
13.3.8. China
13.3.8.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Drug Type (2021-2033)
13.3.8.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Brand (2021-2033)
13.3.8.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Route of Drug Administration (2021-2033)
13.3.8.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Therapeutic Application (2021-2033)
13.3.9. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel (2021-2033)
13.3.10. Japan
13.3.10.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Drug Type (2021-2033)
13.3.10.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Brand (2021-2033)
13.3.10.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Route of Drug Administration (2021-2033)
13.3.10.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Therapeutic Application (2021-2033)
13.3.10.5. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel (2021-2033)
13.3.11. Rest of APAC
13.3.11.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Drug Type (2021-2033)
13.3.11.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Brand (2021-2033)
13.3.11.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Route of Drug Administration (2021-2033)
13.3.11.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Therapeutic Application (2021-2033)
13.3.11.5. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel (2021-2033)
13.4. MEA
13.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Drug Type (2021-2033)
13.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Brand (2021-2033)
13.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Route of Drug Administration (2021-2033)
13.4.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Therapeutic Application (2021-2033)
13.4.5. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel (2021-2033)
13.4.6. GCC
13.4.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Drug Type (2021-2033)
13.4.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Brand (2021-2033)
13.4.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Route of Drug Administration (2021-2033)
13.4.6.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Therapeutic Application (2021-2033)
13.4.7. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel (2021-2033)
13.4.8. North Africa
13.4.8.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Drug Type (2021-2033)
13.4.8.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Brand (2021-2033)
13.4.8.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Route of Drug Administration (2021-2033)
13.4.8.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Therapeutic Application (2021-2033)
13.4.9. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel (2021-2033)
13.4.10. South Africa
13.4.10.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Drug Type (2021-2033)
13.4.10.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Brand (2021-2033)
13.4.10.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Route of Drug Administration (2021-2033)
13.4.10.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Therapeutic Application (2021-2033)
13.4.10.5. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel (2021-2033)
13.4.11. Rest of MEA
13.4.11.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Drug Type (2021-2033)
13.4.11.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Brand (2021-2033)
13.4.11.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Route of Drug Administration (2021-2033)
13.4.11.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Therapeutic Application (2021-2033)
13.4.11.5. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel (2021-2033)
13.5. Latin America
13.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Drug Type (2021-2033)
13.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Brand (2021-2033)
13.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Route of Drug Administration (2021-2033)
13.5.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Therapeutic Application (2021-2033)
13.5.5. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel (2021-2033)
13.5.6. Brazil
13.5.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Drug Type (2021-2033)
13.5.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Brand (2021-2033)
13.5.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Route of Drug Administration (2021-2033)
13.5.6.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Therapeutic Application (2021-2033)
13.5.7. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel (2021-2033)
13.5.8. Rest of LATAM
13.5.8.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Drug Type (2021-2033)
13.5.8.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Brand (2021-2033)
13.5.8.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Route of Drug Administration (2021-2033)
13.5.8.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Therapeutic Application (2021-2033)
13.5.8.5. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel (2021-2033)
Chapter 14. Company Profiles
14.1. Mylan N.V.
14.1.1. Company Overview
14.1.2. Product Offerings
14.1.3. Financial Performance
14.1.4. Recent Initiatives
14.2. Abbott Laboratories
14.2.1. Company Overview
14.2.2. Product Offerings
14.2.3. Financial Performance
14.2.4. Recent Initiatives
14.3. ALLERGAN
14.3.1. Company Overview
14.3.2. Product Offerings
14.3.3. Financial Performance
14.3.4. Recent Initiatives
14.4. Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
14.4.1. Company Overview
14.4.2. Product Offerings
14.4.3. Financial Performance
14.4.4. Recent Initiatives
14.5. Eli Lilly and Company
14.5.1. Company Overview
14.5.2. Product Offerings
14.5.3. Financial Performance
14.5.4. Recent Initiatives
14.6. STADA Arzneimittel AG
14.6.1. Company Overview
14.6.2. Product Offerings
14.6.3. Financial Performance
14.6.4. Recent Initiatives
14.7. GlaxoSmithKline Plc.
14.7.1. Company Overview
14.7.2. Product Offerings
14.7.3. Financial Performance
14.7.4. Recent Initiatives
14.8. Baxter International Inc.
14.8.1. Company Overview
14.8.2. Product Offerings
14.8.3. Financial Performance
14.8.4. Recent Initiatives
14.9. Pfizer Inc.
14.9.1. Company Overview
14.9.2. Product Offerings
14.9.3. Financial Performance
14.9.4. Recent Initiatives
14.10. Sandoz International GmbH
14.10.1. Company Overview
14.10.2. Product Offerings
14.10.3. Financial Performance
14.10.4. Recent Initiatives
Chapter 15. Research Methodology
15.1. Primary Research
15.2. Secondary Research
15.3. Assumptions
Chapter 16. Appendix
16.1. About Us
16.2. Glossary of Terms
 Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
 Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
 Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
 Country/Region-specific Report
Country/Region-specific Report
 Go To Market Strategy
Go To Market Strategy
 Region Specific Market Dynamics
Region Specific Market Dynamics Region Level Market Share
Region Level Market Share Import Export Analysis
Import Export Analysis Production Analysis
Production Analysis Others
Others