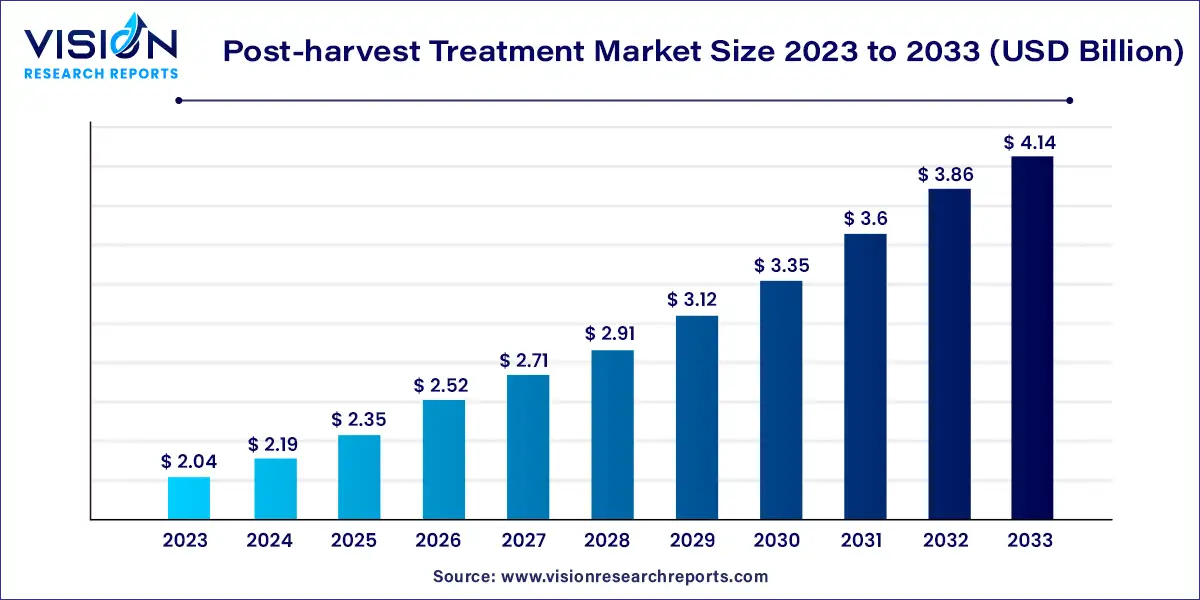
The global post-harvest treatment market size was estimated at around USD 2.04 billion in 2023 and it is projected to hit around USD 4.14 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 7.34% from 2024 to 2033.
The post-harvest treatment market plays a crucial role in ensuring the quality and longevity of agricultural produce after it has been harvested. This market encompasses a range of treatments, technologies, and solutions aimed at preserving freshness, enhancing shelf life, and minimizing post-harvest losses.
At its core, the post-harvest treatment market is driven by the growing demand for efficient and sustainable solutions to address challenges such as spoilage, rot, and decay that can occur during storage, transportation, and distribution. Factors such as increasing global food demand, rising consumer expectations for fresh and high-quality produce, and the need to reduce food waste are key drivers propelling the growth of this market.
The growth of the post-harvest treatment market is driven by an increasing global demand for fresh and high-quality produce is fueling the adoption of post-harvest treatments to preserve freshness and extend shelf life. Additionally, the need to minimize post-harvest losses due to spoilage and decay is pushing farmers and food processors to invest in effective treatment solutions. Furthermore, rising consumer awareness about food safety and sustainability is driving demand for environmentally friendly and residue-free treatment options. Moreover, advancements in technology and research are leading to the development of innovative treatment methods that offer enhanced efficacy and safety. Overall, these factors are contributing to the continued growth and expansion of the post-harvest treatment market worldwide.
The Asia Pacific post-harvest treatment market was estimated at USD 0.85 billion in 2023 and it is expected to surpass around USD 1.73 billion by 2033, poised to grow at a CAGR of 7.36% from 2024 to 2033.
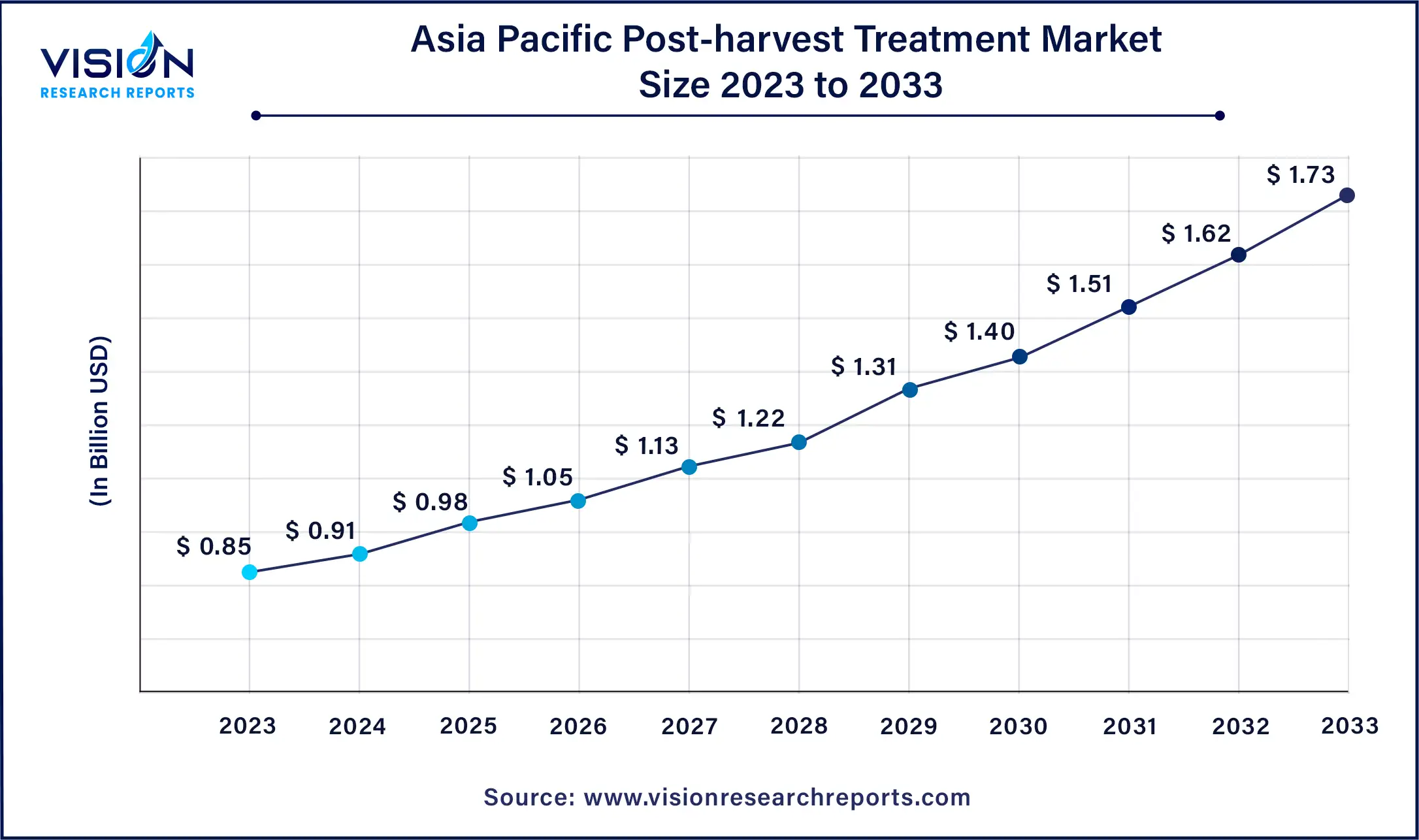
In contrast, Asia Pacific emerged as the dominant market segment in 2023, capturing a significant revenue share of 42%. This dominance is attributed to the region's burgeoning population, resulting in heightened demand for fresh fruits and vegetables. Consequently, the agricultural sector faces increasing pressure to enhance production while minimizing food waste across the supply chain. Leveraging post-harvest treatments becomes crucial in this context, as they play a pivotal role in extending shelf life and reducing spoilage, ensuring a greater quantity of produce reaches consumers.
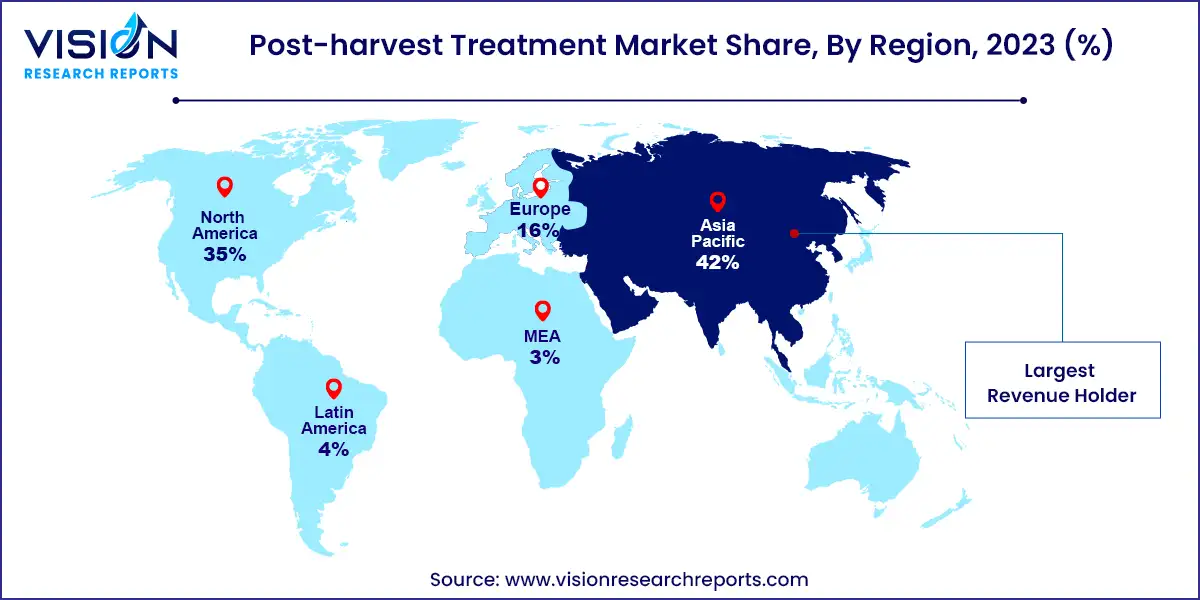
North American consumers exhibit a strong preference for fresh, top-quality fruits and vegetables. This demand is met by post-harvest treatments that effectively preserve the appearance, texture, flavor, and nutritional content of produce, thereby meeting consumer expectations. With busy lifestyles prevalent in the region, there's a notable inclination towards convenient and easily accessible fresh produce. By extending shelf life, these treatments enable consumers to purchase fruits and vegetables less frequently, thus curbing food waste at home.
The coatings segment emerged as the dominant player in the global market, commanding a revenue share of over 32% in 2023. This growth is primarily attributed to its capability to provide a multi-layered approach to extending shelf life and preserving quality. Coatings serve as a thin, physical barrier that minimizes water loss from the produce, thereby helping maintain firmness, texture, and weight.
Moreover, selective coatings facilitate the regulation of gas exchange, including oxygen (O2) and carbon dioxide (CO2), between the fruit or vegetable and its surroundings. This regulation can effectively slow down respiration, a natural process contributing to ripening and spoilage. By prolonging freshness, coatings substantially reduce post-harvest losses, benefiting both producers and consumers alike.
In the realm of post-harvest treatment, cleaners play a crucial role in ensuring the safety and quality of fruits and vegetables. Throughout the harvesting, transportation, and storage processes, produce is susceptible to contamination from various sources such as dirt, debris, insects, and harmful pathogens like bacteria and mold spores. Cleaning procedures effectively remove these contaminants, thereby mitigating the risk of foodborne illness and extending the shelf life of the produce.
In 2023, the fruits and vegetables segment emerged as the dominant force in the global market, owing to its effectiveness in slowing down processes that degrade produce quality. Post-harvest, fruits and vegetables undergo respiration, releasing water vapor and carbon dioxide. This natural process depletes their sugars and nutrients, resulting in wilting, softening, and eventual spoilage. Techniques such as appropriate storage temperatures, controlled atmosphere storage, and coatings are instrumental in slowing down respiration and prolonging shelf life.
Similarly, flowers, despite being cut from the plant, continue biological processes, necessitating post-harvest treatment to preserve their beauty and longevity in a vase. Cut flowers lose water through transpiration, where water vapor is released from their leaves and stems.
To combat this, techniques like stem re-cutting, hydrating solutions, and optimal storage temperatures aid flowers in efficiently absorbing water, thus maintaining their freshness and vibrancy. Loss of water pressure can lead to wilting and bent necks in flowers. Post-harvest treatments, such as support structures and conditioning solutions with precise sugar and acidity levels, help uphold cell turgor (pressure), preventing such issues from occurring.
Based on origin, the synthetic segment dominated the global market in 2023 because it controls spoilage, extends shelf life, and prevents diseases. In some cases, they may be the only proven option for specific fruits and vegetables, especially for long-distance transport or storage. For large-scale producers, synthetic treatments can sometimes be more cost-effective than newer natural alternatives. The infrastructure and application methods for synthetics may already be established, requiring less investment than adopting new technologies.
Many consumers are increasingly concerned about using synthetic chemicals in their food. Natural treatments extend shelf life and maintain quality without artificial preservatives, appealing to health-conscious consumers. Some conventional techniques can leave chemical residues on produce. Natural treatments address this concern, potentially making the food safer for consumers. Natural treatments are often more environmentally friendly than conventional methods. They may not require as much energy or generate harmful byproducts, reducing the environmental impact of food production.
While the trend is toward natural options, some consumers may not be willing to pay a premium for them. This can influence producer decisions, especially for large retailers and supermarkets with tight profit margins. Some natural treatments may require additional infrastructure or equipment that small-scale farmers may not have access to or cannot afford. Synthetics may be a more practical option in such cases.
By Type
By Crop Type
By Origin
By Region
Chapter 1. Introduction
1.1. Research Objective
1.2. Scope of the Study
1.3. Definition
Chapter 2. Research Methodology
2.1. Research Approach
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Assumptions & Limitations
Chapter 3. Executive Summary
3.1. Market Snapshot
Chapter 4. Market Variables and Scope
4.1. Introduction
4.2. Market Classification and Scope
4.3. Industry Value Chain Analysis
4.3.1. Raw Material Procurement Analysis
4.3.2. Sales and Distribution Type Analysis
4.3.3. Downstream Buyer Analysis
Chapter 5. COVID 19 Impact on Post-harvest Treatment Market
5.1. COVID-19 Landscape: Post-harvest Treatment Industry Impact
5.2. COVID 19 - Impact Assessment for the Industry
5.3. COVID 19 Impact: Global Major Government Policy
5.4. Market Trends and Opportunities in the COVID-19 Landscape
Chapter 6. Market Dynamics Analysis and Trends
6.1. Market Dynamics
6.1.1. Market Drivers
6.1.2. Market Restraints
6.1.3. Market Opportunities
6.2. Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
6.2.1. Bargaining power of suppliers
6.2.2. Bargaining power of buyers
6.2.3. Threat of substitute
6.2.4. Threat of new entrants
6.2.5. Degree of competition
Chapter 7. Competitive Landscape
7.1.1. Company Market Share/Positioning Analysis
7.1.2. Key Strategies Adopted by Players
7.1.3. Vendor Landscape
7.1.3.1. List of Suppliers
7.1.3.2. List of Buyers
Chapter 8. Global Post-harvest Treatment Market, By Type
8.1. Post-harvest Treatment Market, by Type, 2024-2033
8.1.1 Coatings
8.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
8.1.2. Cleaners
8.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
8.1.3. Fungicides
8.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
8.1.4. Ethylene Blockers
8.1.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
8.1.5. Other Types
8.1.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
Chapter 9. Global Post-harvest Treatment Market, By Crop Type
9.1. Post-harvest Treatment Market, by Crop Type, 2024-2033
9.1.1. Fruits & Vegetables
9.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
9.1.2. Fruits & Ornamentals
9.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
9.1.3. Other Crop types
9.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
Chapter 10. Global Post-harvest Treatment Market, By Origin
10.1. Post-harvest Treatment Market, by Origin, 2024-2033
10.1.1. Natural
10.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
10.1.2. Synthetic
10.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
Chapter 11. Global Post-harvest Treatment Market, Regional Estimates and Trend Forecast
11.1. North America
11.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type (2021-2033)
11.1.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Crop Type (2021-2033)
11.1.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Origin (2021-2033)
11.1.4. U.S.
11.1.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type (2021-2033)
11.1.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Crop Type (2021-2033)
11.1.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Origin (2021-2033)
11.1.5. Rest of North America
11.1.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type (2021-2033)
11.1.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Crop Type (2021-2033)
11.1.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Origin (2021-2033)
11.2. Europe
11.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type (2021-2033)
11.2.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Crop Type (2021-2033)
11.2.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Origin (2021-2033)
11.2.4. UK
11.2.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type (2021-2033)
11.2.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Crop Type (2021-2033)
11.2.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Origin (2021-2033)
11.2.5. Germany
11.2.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type (2021-2033)
11.2.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Crop Type (2021-2033)
11.2.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Origin (2021-2033)
11.2.6. France
11.2.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type (2021-2033)
11.2.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Crop Type (2021-2033)
11.2.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Origin (2021-2033)
11.2.7. Rest of Europe
11.2.7.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type (2021-2033)
11.2.7.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Crop Type (2021-2033)
11.2.7.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Origin (2021-2033)
11.3. APAC
11.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type (2021-2033)
11.3.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Crop Type (2021-2033)
11.3.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Origin (2021-2033)
11.3.4. India
11.3.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type (2021-2033)
11.3.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Crop Type (2021-2033)
11.3.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Origin (2021-2033)
11.3.5. China
11.3.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type (2021-2033)
11.3.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Crop Type (2021-2033)
11.3.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Origin (2021-2033)
11.3.6. Japan
11.3.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type (2021-2033)
11.3.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Crop Type (2021-2033)
11.3.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Origin (2021-2033)
11.3.7. Rest of APAC
11.3.7.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type (2021-2033)
11.3.7.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Crop Type (2021-2033)
11.3.7.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Origin (2021-2033)
11.4. MEA
11.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type (2021-2033)
11.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Crop Type (2021-2033)
11.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Origin (2021-2033)
11.4.4. GCC
11.4.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type (2021-2033)
11.4.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Crop Type (2021-2033)
11.4.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Origin (2021-2033)
11.4.5. North Africa
11.4.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type (2021-2033)
11.4.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Crop Type (2021-2033)
11.4.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Origin (2021-2033)
11.4.6. South Africa
11.4.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type (2021-2033)
11.4.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Crop Type (2021-2033)
11.4.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Origin (2021-2033)
11.4.7. Rest of MEA
11.4.7.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type (2021-2033)
11.4.7.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Crop Type (2021-2033)
11.4.7.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Origin (2021-2033)
11.5. Latin America
11.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type (2021-2033)
11.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Crop Type (2021-2033)
11.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Origin (2021-2033)
11.5.4. Brazil
11.5.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type (2021-2033)
11.5.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Crop Type (2021-2033)
11.5.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Origin (2021-2033)
11.5.5. Rest of LATAM
11.5.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type (2021-2033)
11.5.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Crop Type (2021-2033)
11.5.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Origin (2021-2033)
Chapter 12. Company Profiles
12.1. JBT.
12.1.1. Company Overview
12.1.2. Product Offerings
12.1.3. Financial Performance
12.1.4. Recent Initiatives
12.2. Syngenta Crop Protection.
12.2.1. Company Overview
12.2.2. Product Offerings
12.2.3. Financial Performance
12.2.4. Recent Initiatives
12.3. Nufarm.
12.3.1. Company Overview
12.3.2. Product Offerings
12.3.3. Financial Performance
12.3.4. Recent Initiatives
12.4. Bayer AG.
12.4.1. Company Overview
12.4.2. Product Offerings
12.4.3. Financial Performance
12.4.4. Recent Initiatives
12.5. BASF SE.
12.5.1. Company Overview
12.5.2. Product Offerings
12.5.3. Financial Performance
12.5.4. Recent Initiatives
12.6. Citrosol
12.6.1. Company Overview
12.6.2. Product Offerings
12.6.3. Financial Performance
12.6.4. Recent Initiatives
12.7. Hazel Technologies Inc.
12.7.1. Company Overview
12.7.2. Product Offerings
12.7.3. Financial Performance
12.7.4. Recent Initiatives
12.8. Lytone Enterprise Inc.
12.8.1. Company Overview
12.8.2. Product Offerings
12.8.3. Financial Performance
12.8.4. Recent Initiatives
12.9. Janssen PNP.
12.9.1. Company Overview
12.9.2. Product Offerings
12.9.3. Financial Performance
12.9.4. Recent Initiatives
12.10. Futureco Chemicals Inc.
12.10.1. Company Overview
12.10.2. Product Offerings
12.10.3. Financial Performance
12.10.4. Recent Initiatives
Chapter 13. Research Methodology
13.1. Primary Research
13.2. Secondary Research
13.3. Assumptions
Chapter 14. Appendix
14.1. About Us
14.2. Glossary of Terms
 Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
 Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
 Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
 Country/Region-specific Report
Country/Region-specific Report
 Go To Market Strategy
Go To Market Strategy
 Region Specific Market Dynamics
Region Specific Market Dynamics Region Level Market Share
Region Level Market Share Import Export Analysis
Import Export Analysis Production Analysis
Production Analysis Others
Others