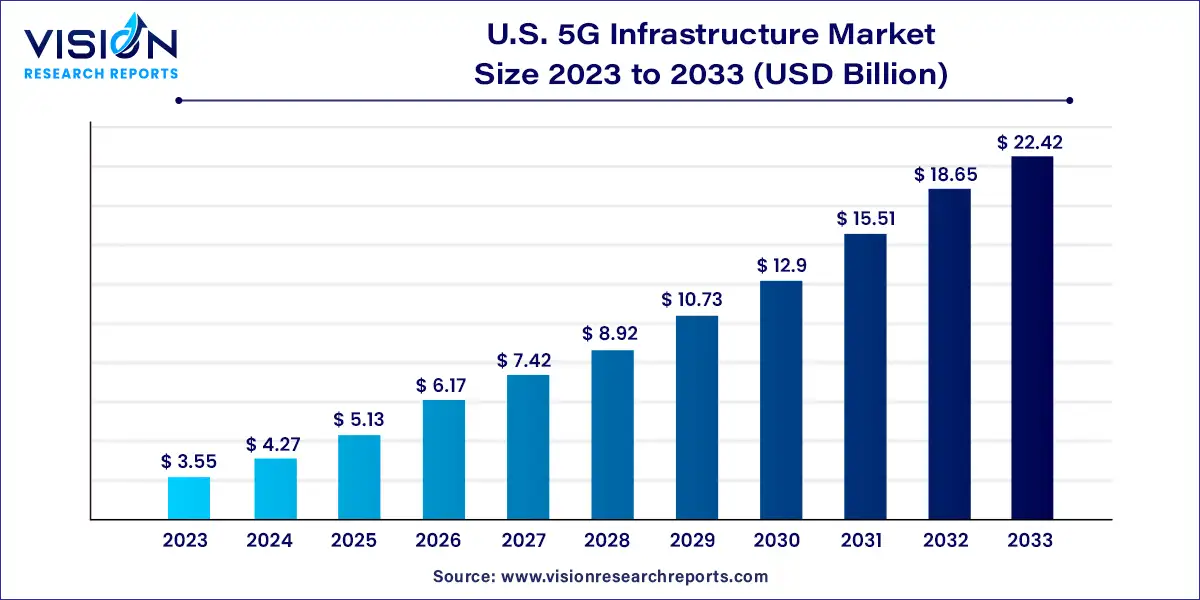
The U.S. 5G infrastructure market size was estimated at around USD 3.55 billion in 2023 and it is projected to hit around USD 22.42 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 20.24% from 2024 to 2033.
The emergence of 5G technology has sparked a revolution in connectivity, promising faster speeds, lower latency, and greater capacity. In the United States, the race to deploy robust 5G infrastructure is well underway, with telecom companies, technology firms, and policymakers collaborating to usher in this new era of connectivity.
The growth of the U.S. 5G infrastructure market is propelled by the burgeoning demand for high-speed, low-latency connectivity, driven by an increasing reliance on bandwidth-intensive applications such as IoT, AR, VR, autonomous vehicles, and telemedicine. Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic has underscored the critical need for robust broadband connectivity, accelerating the adoption of 5G technology for remote work, distance learning, and telehealth services. Furthermore, strategic investments by telecom operators and technology firms, coupled with supportive regulatory initiatives such as the FCC's 5G Fast Plan, are driving rapid deployment and expansion of 5G networks across the nation. These growth factors collectively contribute to the thriving landscape of the U.S. 5G infrastructure market, promising significant opportunities for stakeholders across the ecosystem.
In 2023, the sub-6 GHz segment dominated with a revenue share of 72%. Networks within this segment operate between 1 GHz to 6 GHz, with 3.5 GHz being globally recognized as the most prevalent frequency. While mmWave technology promises significantly faster speeds, its reliability is often compromised by obstacles, limiting its range. In contrast, the sub-6 GHz spectrum boasts reliability and a longer range, albeit with slower speeds, as it utilizes older 4G-like frequencies. Consequently, major smartphone and chip manufacturers prefer incorporating sub-6 GHz 5G network support into their products. Moreover, technologies like massive MIMO and beamforming further enhance signal quality in this segment.
The mmWave technology segment is projected to experience the fastest growth during the forecast period. Notably, mmWave offers connectivity speeds surpassing 1 Gbps. With a rising population of streamers and gamers in the U.S., there's a growing demand for higher speeds and lower latency, which is expected to propel the focus on the mmWave spectrum in the coming years. Additionally, industries are seeking this segment due to the increased deployment of factory robots and automated guided vehicles (AGVs) requiring low latency and high bandwidth for efficient operations. A survey conducted by Counterpoint among U.S. smartphone users revealed that 60% of respondents considered 5G mmWave capability when purchasing a 5G smartphone, indicating its increasing adoption in the country.
In 2023, the hardware segment commanded the largest revenue share at 78%. Within this segment, Radio Access Network (RAN) plays a pivotal role, driving significant demand. Notably, substantial investments in RAN infrastructure and the increasing adoption of Open RAN (O-RAN) across the U.S. are anticipated to fuel growth in this segment. Companies are turning to professional services to effectively adopt and integrate 5G RAN into their existing network infrastructure, further propelling this growth trajectory. In February 2024, the government announced a USD 42 million investment to advance the development of 5G O-RAN standards, aiming to provide wireless providers with more software and hardware options. Such initiatives are poised to stimulate demand for hardware components.
The MidHaul sub-segment is projected to experience the swiftest growth within the hardware segment through 2033. Traditionally, in 4G architecture, the Distributed Radio Access Network (D-RAN) architecture places the baseband unit (BBU) at the base of a macro cell tower. However, in 5G infrastructure, the 5G RAN transitions from the Remote Radio Head and traditional BBU to a Centralized Unit (CU), Active Antenna Unit, and Distributed Unit (DU) architecture. Here, MidHaul denotes the link between the Data Center (DC) and CU. The MidHaul transport network is expected to meet performance requirements supporting reaches of up to 100 km with latency of 5 milliseconds or less. Companies are deploying MidHaul infrastructure to enhance user experience, driving growth in this sub-segment over the forecast period.
In 2023, the non-standalone segment dominated with the largest revenue share of 82%. This architecture provides an economical option by leveraging existing 4G infrastructure to enhance Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB) services without requiring a complete infrastructure overhaul. Mobile network operators aiming to deliver high-speed connectivity to customers via 5G-enabled devices find the non-standalone architecture particularly beneficial. Leading wireless providers in the U.S., including Verizon and AT&T, have adopted non-standalone networks to offer 5G services for applications such as AR/VR gaming and UHD video streaming, driving segment expansion.
The standalone segment is expected to witness the fastest growth rate through 2033, primarily fueled by initiatives to develop standalone 5G infrastructure in the United States. For instance, AT&T Labs recently announced the development of an industry-first 5G SA Uplink 2-carrier aggregation data call, aimed at providing more reliable services to customers. Standalone architecture utilizes a dedicated 5G core, offering advantages such as ultra-low latency, faster upload speeds, high reliability, and edge functions. The increasing adoption of connected technologies and concepts like smart factories is projected to significantly propel segment growth in the coming years.
In 2023, the enterprise/corporate segment claimed the largest revenue share at 21%, as businesses increasingly recognize the importance of higher data bandwidth to enhance productivity. 5G technology enables seamless movement of large data volumes without network issues, while its low-latency feature is crucial for businesses leveraging IoT applications. Moreover, the COVID-19 pandemic has heightened consumer expectations for a seamless digital experience from enterprises, driving 5G adoption in this sector. The surge in virtual meetings and cloud computing underscores the necessity of 5G, as these platforms rely on reliable and uninterrupted connectivity for effective data exchange and communication.
The industrial segment is poised to experience the fastest CAGR from 2024 to 2033. The U.S. is witnessing a rapid uptake of concepts such as smart factories and Industrial IoT, highlighting the demand for high-speed wireless connectivity. The widespread adoption of drones, sensors, and automated guided vehicles (AGVs) to enhance efficiency and employee safety is fueling the adoption of advanced 5G infrastructure. Furthermore, 5G facilitates faster and more accurate data collection from equipment and machinery sensors, optimizing maintenance scheduling, prolonging longevity, and significantly reducing process disruptions. These factors are expected to play a decisive role in the increased deployment of 5G in industrial settings.
By Component
By Spectrum
By Network Architecture
By Vertical
 Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
 Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
 Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
 Country/Region-specific Report
Country/Region-specific Report
 Go To Market Strategy
Go To Market Strategy
 Region Specific Market Dynamics
Region Specific Market Dynamics Region Level Market Share
Region Level Market Share Import Export Analysis
Import Export Analysis Production Analysis
Production Analysis Others
Others