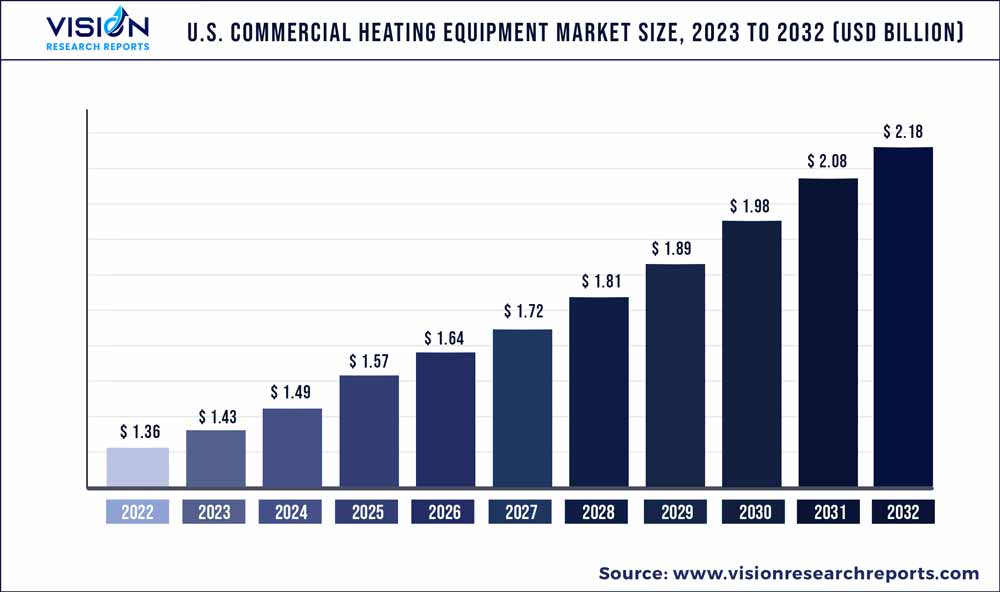
The U.S. commercial heating equipment market was surpassed at USD 1.36 billion in 2022 and is expected to hit around USD 2.18 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 4.84% from 2023 to 2032.
Key Pointers
Report Scope of the U.S. Commercial Heating Equipment Market
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2022 | USD 1.36 billion |
| Revenue Forecast by 2032 | USD 2.18 billion |
| Growth rate from 2023 to 2032 | CAGR of 4.84% |
| Base Year | 2022 |
| Forecast Period | 2023 to 2032 |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Companies Covered | Carrier Corporation; Mitsubishi Electric Corporation,;Emerson Electric Co.; Ingersoll-Rand Plc; Daikin Industries, Ltd.; Rheem Manufacturing, Lennox Inernational; Johnson Controls, Inc.; Robert Bosch GmbH; Viesmann Group |
The favorable government initiatives such as rebates and incentives for the installation of highly energy-efficient heating products such as heat pumps are projected to have a positive impact on the market.
The increasing adoption of heat pumps in retail shops, hotels, offices, and healthcare facilities is projected to boost the demand for heat pumps in the commercial sector over the forecast period. Furthermore, in all climates, heat pumps provide an energy-efficient replacement for furnaces and air conditioners. When compared to traditional heating or cooling equipment, heat pumps can provide an identical level of area conditioning at a fourth of the operational cost.
The heating equipment enclosures are often constructed from various metal sheets that have been cut to the correct dimensions and bent into various forms and configurations. Tube bending machines bend thin copper or aluminum tubes around curved dies to form condensers and evaporators. These tubes function as heat exchangers by allowing working fluids to circulate through them. Heat pumps, on the other hand, comprise other components such as tubes, brackets, and valves. This heating equipment is coated with corrosion-resistant paints or powders.
The market is extremely competitive, and the companies operating in this market face the risk of losing their businesses due to a variety of reasons, such as price changes, product performance, geographic presence, and customer services. External factors such as variations in commercial construction activities, changes in regulations, fluctuations in labor costs, variations in interest rates, and volatility in foreign currency exchange rates, along with the impact of various political issues, also significantly affect the revenues of commercial heating equipment manufacturers.
End users of heating equipment in the U.S. comprise residential, commercial, and industrial establishments. Residential establishments utilize heating systems for space heating, water heating, and other utility purposes, while commercial and industrial establishments require heating equipment for manufacturing, space heating, and smelting processes. Industrial buyers focus on factors such as energy and operational cost savings, maintenance cost, and product lifespan while purchasing heating equipment.
Product Insights
The heat pump product segment led the market and accounted for 34.14% of the market revenue share in 2022. Heat pumps are widely used in regions that require moderate heating and cooling. Heat pumps are also known as two-way air conditioners because they help extract heat from cold outdoors with the help of an electrical system and discharge that heat inside the house. In summer, the operations of a heat pump are reversed, which helps keep the interiors cooler by extracting heat from indoors.
Commercial heat pump systems are confined to heat supply temperatures ranging from up to 80°C but industrial operations are frequently built for heat supply temperatures ranging from 100°C to 200°C. In addition, heat pumps are the ideal design choice for commercial applications that require heat pump energy yield at temperatures up to 80°C. Commercial heat pump systems provide the necessary plant benefits for any application requiring delivery performance, energy savings, and high-temperature output.
Furnaces are utilized in establishments that require high-temperature heating. Furnaces heat the air and use ducts to circulate it throughout the facility. A propane furnace is a versatile machine that can meet the heating requirements of any commercial building. Smaller capacity propane furnaces may even be eligible for Energy Star's Most Efficient certification, which corresponds to energy savings of 20% or more over a normal furnace. In addition to high-efficiency equipment, appropriately sized furnaces contribute to efficiency by lowering energy expenditures and extending equipment life. Heat for the furnace can be provided directly by burning fuel, electricity, or induction heating. Propane furnaces are versatile, in terms of both kind and capacity, making them suitable for a wide range of commercial buildings. Gas and electric furnaces are the most common in commercial applications.
Boilers heat water and transmit hot water or steam for a variety of applications. Steam is delivered to steam radiators via pipes; hot water can heat air via a coil. Water heating, power generation, cooking, central heating, and sanitation are among the applications of boilers. Commercial boilers use combustible fuel to heat water, converting the liquid water into steam, which is then dispersed to provide heating in a building or other structure. These aforementioned factors are expected to drive the demand for boilers in the coming years. For instance, Ideal Commercial provides wall-hung, floor-standing, and modular condensing commercial boilers in compact designs.
Unitary heaters are commonly utilized in the commercial sector to address the space heating needs of small complexes or rooms. Unitary heaters have a low starting cost and an easy installation procedure. These reasons are expected to fuel market growth in the coming years. For instance, Warren Technologies provides unitary heaters in various sizes, shapes, and configurations that can be field mounted in any brand of air conditioning system.
Building Floorspace Insights
Building floorspace up to 5,000 sq. ft. segment accounted for 42.26% of the U.S. commercial heating equipment revenue share in 2022. Stores, schools, offices, places of worship, libraries, hospitals, gymnasiums, museums, clinics, and warehouses are all examples of commercial structures. Commercial building design, construction, use, and demolition have an impact on the environment, worker productivity, and community well-being. Increasing commercial building floor space of up to 5,000 square feet will demand more commercial construction which will further propel the demand for heating equipment as they assist in reducing energy waste while lowering operating costs and improving comfort.
In the U.S., there are 5.6 million commercial buildings with 51 billion square feet to 87 billion square feet of floor space. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, there are 5.6 million commercial structures with a combined 87 billion square feet of floor space in the country, which represents an increase of 3.8 million commercial buildings in 2021. More structures are needed due to an increasing population and shifting consumer demands.
Around 45% of building emissions are currently caused by heating equipment, which sources more than 55% of its total energy needs from fossil fuels. Three-quarters of the carbon emissions reductions required in the construction sector under the Sustainable Development Scenario can be accomplished through the broad adoption of technologies such as the electrification of heating equipment. For instance, targeting buildings larger than 10,000 square feet for electrification will have a significant influence on lowering carbon emissions because they make up 82% of total commercial floor space in the U.S.
U.S. Commercial Heating Equipment Market Segmentations:
By Product
By Building Floorspace
Chapter 1. Introduction
1.1. Research Objective
1.2. Scope of the Study
1.3. Definition
Chapter 2. Research Methodology
2.1. Research Approach
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Assumptions & Limitations
Chapter 3. Executive Summary
3.1. Market Snapshot
Chapter 4. Market Variables and Scope
4.1. Introduction
4.2. Market Classification and Scope
4.3. Industry Value Chain Analysis
4.3.1. Raw Material Procurement Analysis
4.3.2. Sales and Distribution Channel Analysis
4.3.3. Downstream Buyer Analysis
Chapter 5. COVID 19 Impact on U.S. Commercial Heating Equipment Market
5.1. COVID-19 Landscape: U.S. Commercial Heating Equipment Industry Impact
5.2. COVID 19 - Impact Assessment for the Industry
5.3. COVID 19 Impact: Major Government Policy
5.4. Market Trends and Opportunities in the COVID-19 Landscape
Chapter 6. Market Dynamics Analysis and Trends
6.1. Market Dynamics
6.1.1. Market Drivers
6.1.2. Market Restraints
6.1.3. Market Opportunities
6.2. Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
6.2.1. Bargaining power of suppliers
6.2.2. Bargaining power of buyers
6.2.3. Threat of substitute
6.2.4. Threat of new entrants
6.2.5. Degree of competition
Chapter 7. Competitive Landscape
7.1.1. Company Market Share/Positioning Analysis
7.1.2. Key Strategies Adopted by Players
7.1.3. Vendor Landscape
7.1.3.1. List of Suppliers
7.1.3.2. List of Buyers
Chapter 8. U.S. Commercial Heating Equipment Market, By Product
8.1. U.S. Commercial Heating Equipment Market, by Product, 2023-2032
8.1.1. Heat Pump
8.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2020-2032)
8.1.2. Furnace
8.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2020-2032)
8.1.3. Boiler
8.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2020-2032)
8.1.4. Unitary Heaters
8.1.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2020-2032)
8.1.5. Others
8.1.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2020-2032)
Chapter 9. U.S. Commercial Heating Equipment Market, By Building Floorspace
9.1. U.S. Commercial Heating Equipment Market, by Building Floorspace, 2023-2032
9.1.1. Up to 5,000 sq. ft.
9.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2020-2032)
9.1.2. 5,001 to 10,000 sq. ft
9.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2020-2032)
9.1.3. 10,001 to 25,000 sq. ft
9.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2020-2032)
9.1.4. 25,001 to 50,000 sq. ft
9.1.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2020-2032)
9.1.5. 50,001 to 100,000 sq. ft
9.1.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2020-2032)
9.1.6. above 100,000 sq. ft
9.1.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2020-2032)
Chapter 10. U.S. Commercial Heating Equipment Market, Regional Estimates and Trend Forecast
10.1. U.S.
10.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product (2020-2032)
10.1.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Building Floorspace (2020-2032)
Chapter 11. Company Profiles
11.1. Carrier Corporation
11.1.1. Company Overview
11.1.2. Product Offerings
11.1.3. Financial Performance
11.1.4. Recent Initiatives
11.2. Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
11.2.1. Company Overview
11.2.2. Product Offerings
11.2.3. Financial Performance
11.2.4. Recent Initiatives
11.3. Emerson Electric Co.
11.3.1. Company Overview
11.3.2. Product Offerings
11.3.3. Financial Performance
11.3.4. Recent Initiatives
11.4. Ingersoll-Rand Plc
11.4.1. Company Overview
11.4.2. Product Offerings
11.4.3. Financial Performance
11.4.4. LTE Scientific
11.5. Daikin Industries, Ltd.
11.5.1. Company Overview
11.5.2. Product Offerings
11.5.3. Financial Performance
11.5.4. Recent Initiatives
11.6. Rheem Manufacturing
11.6.1. Company Overview
11.6.2. Product Offerings
11.6.3. Financial Performance
11.6.4. Recent Initiatives
11.7. Lennox Inernational
11.7.1. Company Overview
11.7.2. Product Offerings
11.7.3. Financial Performance
11.7.4. Recent Initiatives
11.8. Johnson Controls, Inc.
11.8.1. Company Overview
11.8.2. Product Offerings
11.8.3. Financial Performance
11.8.4. Recent Initiatives
11.9. Robert Bosch GmbH
11.9.1. Company Overview
11.9.2. Product Offerings
11.9.3. Financial Performance
11.9.4. Recent Initiatives
11.10. Viesmann Group
11.10.1. Company Overview
11.10.2. Product Offerings
11.10.3. Financial Performance
11.10.4. Recent Initiatives
Chapter 12. Research Methodology
12.1. Primary Research
12.2. Secondary Research
12.3. Assumptions
Chapter 13. Appendix
13.1. About Us
13.2. Glossary of Terms
 Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
 Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
 Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
 Country/Region-specific Report
Country/Region-specific Report
 Go To Market Strategy
Go To Market Strategy
 Region Specific Market Dynamics
Region Specific Market Dynamics Region Level Market Share
Region Level Market Share Import Export Analysis
Import Export Analysis Production Analysis
Production Analysis Others
Others