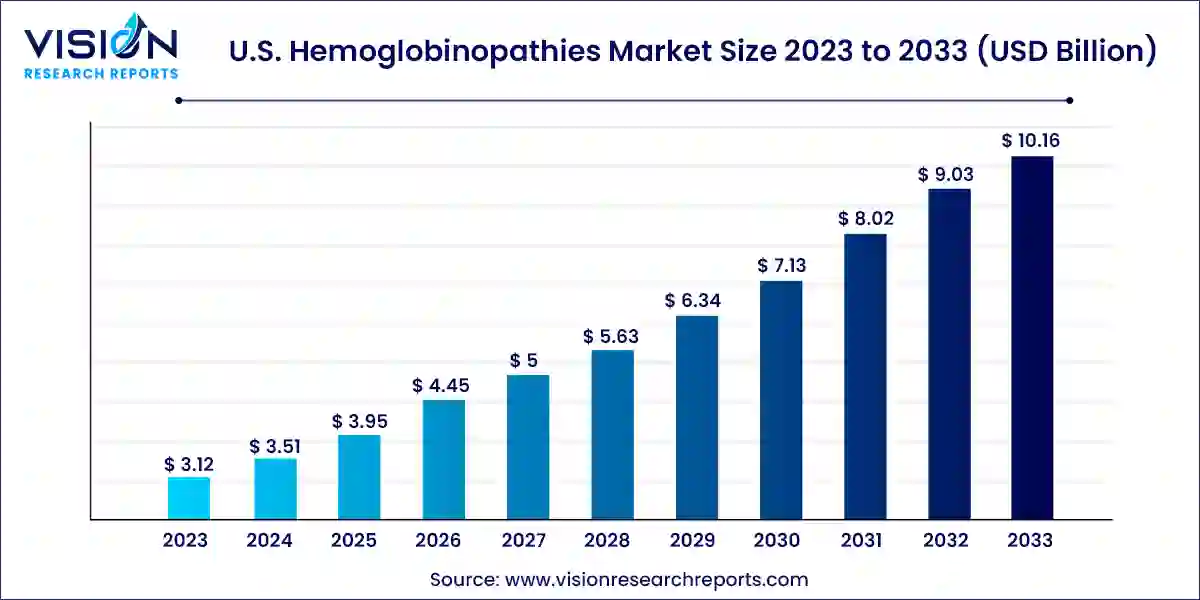
The U.S. hemoglobinopathies market size was estimated at USD 3.12 billion in 2023 and it is expected to surpass around USD 10.16 billion by 2033, poised to grow at a CAGR of 12.53% from 2024 to 2033.
Hemoglobinopathies represent a group of inherited blood disorders characterized by abnormalities in the structure or production of hemoglobin, the molecule in red blood cells responsible for carrying oxygen. In the United States, hemoglobinopathies pose significant health challenges, affecting millions of individuals and necessitating comprehensive approaches to diagnosis, management, and treatment.
The growth of the U.S. hemoglobinopathies market is propelled by an advancements in genetic screening technologies have facilitated early detection and diagnosis of hemoglobinopathies, leading to improved patient outcomes. Additionally, ongoing research and development efforts have resulted in the introduction of innovative therapeutic modalities, including gene therapies and targeted treatments, which hold promise for addressing unmet medical needs. Furthermore, regulatory initiatives aimed at expediting the approval process for investigational therapies have accelerated market access for novel treatments.
Sickle cell disease held the majority share of 61% in the market in 2023 and is projected to exhibit the fastest CAGR throughout the forecast period. The growth is primarily fueled by increased initiatives from biopharmaceutical companies and nonprofit organizations, aimed at enhancing access to Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) treatment. Moreover, awareness campaigns emphasizing disease diagnosis play a pivotal role in propelling market expansion. Notably, in the U.S., various organizations prioritize promoting early diagnosis and providing support to those affected by sickle cell disease. Key players in these efforts include the Sickle Cell Disease Association of America (SCDAA) and its local chapters, which organize educational events, community workshops, and health fairs to raise awareness and facilitate early detection of sickle cell disease.
Additionally, ongoing scientific trials are assessing the safety and efficacy of potential therapies for hemoglobinopathies. These trials involve testing new drugs or treatments on patients to evaluate their benefits, risks, and optimal usage. By generating robust data on treatment effectiveness, scientific trials inform clinical decision-making and regulatory approval processes, contributing to segment growth in the country.
Sickle cell disease accounted for the largest share of market revenue in 2023 and is anticipated to witness the fastest CAGR over the forecast period. Recent years have witnessed a significant trend in the sickle cell disease diagnosis market towards the development and adoption of innovative diagnostic technologies. These advancements include genetic testing methods such as next-generation sequencing and molecular diagnostics, which have substantially enhanced the accuracy and efficiency of sickle cell disease identification and variant detection. Point-of-care testing (POCT) devices and rapid diagnostic kits have also gained popularity in various healthcare settings, enabling rapid and convenient screening, facilitating quicker decision-making, and potentially improving patient outcomes.
Moreover, there has been a notable increase in focus on newborn screening programs for hemoglobinopathies, genetic disorders affecting hemoglobin structure. This heightened emphasis aims to ensure early detection of these disorders, enabling timely interventions and improving patient outcomes. By integrating advanced screening methods into newborn care, healthcare providers can effectively identify and manage hemoglobinopathies like sickle cell disease and thalassemia, thereby enhancing treatment efficacy and patient well-being.
In 2023, the sickle cell disease segment dominated the market and is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR over the forecast period. The advancement and approval of innovative therapies, including gene therapies and targeted treatments designed to modify genetic abnormalities or address disease symptoms, significantly contribute to market growth. Stem cell transplantation, particularly from matched unrelated donors, is increasingly recognized as a viable curative option. Additionally, there is growing emphasis on supportive care strategies such as pain management, infection prevention, and hydroxyurea therapy. The shift towards personalized medicine approaches and patient-centered care models is gaining momentum, aiming to enhance treatment outcomes for individuals with sickle cell disease.
Blood transfusions represent a primary treatment method for hemoglobin disorders, including thalassemia and related conditions. These transfusions are particularly crucial for patients with thalassemia, who often require more frequent transfusions than those with other hemoglobinopathies, aiming to maintain normal blood component levels and alleviate associated symptoms. Typically, blood transfusions are administered every 3 to 4 weeks.
Bone marrow transplant (BMT) therapy is poised for significant growth in the upcoming period, especially as a treatment of choice when conventional therapies like blood transfusions prove ineffective. BMT demonstrates efficacy, particularly in the early stages of disease progression, offering a solution for patients struggling to produce a sufficient number of healthy cells. By introducing healthy stem cells into the patient’s body, BMT aims to replace diseased or damaged bone marrow, increasingly utilized in managing severe cases of sickle cell disease and thalassemia
By Type
By Diagnosis
By Therapy
By Region
 Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
 Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
 Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
 Country/Region-specific Report
Country/Region-specific Report
 Go To Market Strategy
Go To Market Strategy
 Region Specific Market Dynamics
Region Specific Market Dynamics Region Level Market Share
Region Level Market Share Import Export Analysis
Import Export Analysis Production Analysis
Production Analysis Others
Others