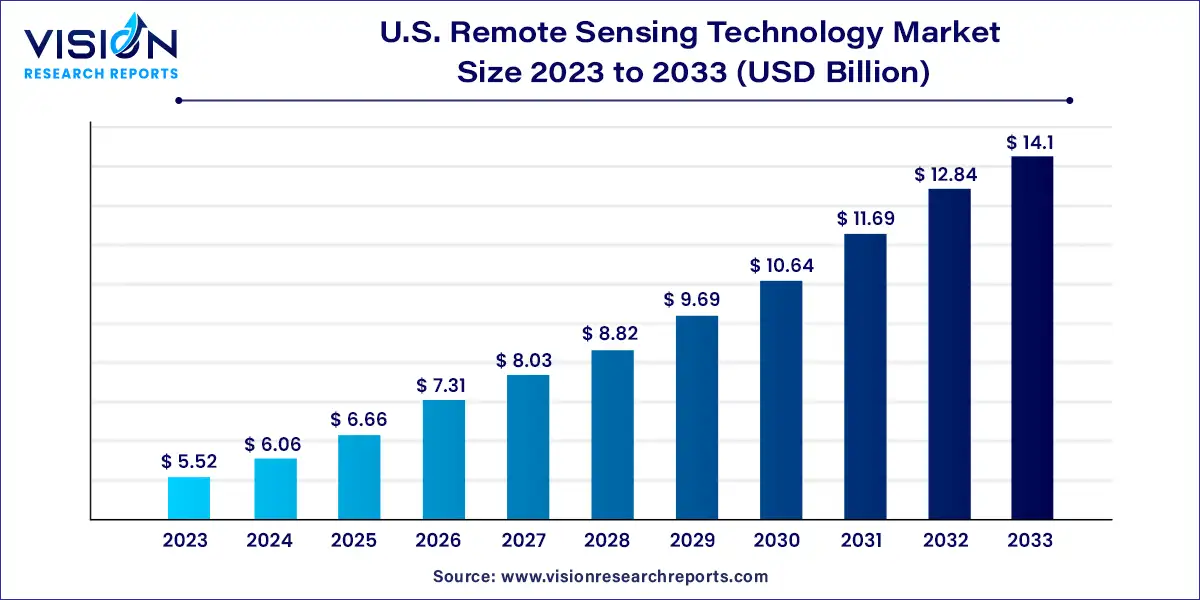
The U.S. remote sensing technology market size was estimated at USD 5.52 billion in 2023 and it is expected to surpass around USD 14.1 billion by 2033, poised to grow at a CAGR of 9.83% from 2024 to 2033. The U.S. remote sensing technology market has witnessed significant growth over the past decade, driven by advancements in satellite and sensor technologies, increased demand for environmental monitoring, and a growing focus on national security. This market encompasses various technologies used to collect, analyze, and interpret data from a distance, typically through satellites, drones, or airborne sensors.
The U.S. remote sensing technology market is propelled by several key growth factors that contribute to its expanding influence across various sectors. One of the primary drivers is the rapid advancement in satellite and sensor technologies, which have significantly enhanced data accuracy, resolution, and coverage. This technological progress enables more detailed and reliable monitoring of environmental changes, agricultural conditions, and urban development. Additionally, the increasing emphasis on environmental sustainability and climate change mitigation fuels the demand for precise and timely data, which remote sensing technologies provide. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning further amplifies the capabilities of these technologies, facilitating more efficient data processing and analysis.
The passive remote sensing segment accounted for the largest market share of over 60% in 2023 and is anticipated to register the highest CAGR over the forecast period. Most passive systems for remote sensing applications operate in the electromagnetic spectrum's thermal, visible, infrared, and microwave ranges. Also, to monitor and assess the Earth's surface features, passive remote sensing technology examines the sunlight reflected from the Earth's surface. Since the technology delivers high-quality satellite photos, numerous applications for Earth observation rely on it.
The active remote sensing segment is expected to grow at a considerable CAGR over the forecast period. Active remote sensing technology is frequently used to assess the topography of oceans, ice, and forests, among others. Active sensors allow measurements to be taken at any time, irrespective of the time of day or season. They can be used to better regulate how a target is lighted or to examine wavelengths that are insufficiently offered by the Sun, such as microwaves.
The military and intelligence segment accounted for the largest market share of nearly 34% in 2023. Military decision-makers rely on remote sensing technologies to provide precise information about the target location, the vicinity of civilian areas, weather information, and terrain analysis. Moreover, the increasing need for battlefield management, which involves integrating, tracking, and processing data to improve the effectiveness of command and control in military operations, is expected to drive the segment’s growth. The way wartime fights are organized has transformed due to the use of remote sensing technology. For digital mapping, planning of combat operations, and command control, the military commander in a conflict uses spatial data and Geographic Information System (GIS) technologies.
The disaster management segment is expected to register the fastest CAGR over the forecast period. Natural disasters occur frequently due to events such as earthquakes, volcanoes, and floods. Remote sensing can support risk reduction operations by locating risk areas related to floodplains, coastal erosion and inundation, and active faults. Determining the location and scale of actual incidents can also be used to validate hazard models. Distant sensors can detect the onset of an earthquake by providing essential information to estimate the locations that will be impacted.
Remote sensing technology is crucial in emergency mapping to facilitate a simple and rapid catastrophe response. The emergency crew uses the massive, widespread, and fast data provided by the sensors to organize their rescue operation. The use of remote sensing in damage assessment and recovery following a disaster can transform how disasters are managed completely. It can offer precise, timely details regarding the degree of damage, the type of debris present, and the quantity of resources required for an effective recovery.
The aerial systems segment accounted for the largest market share of over 71% in 2023. The aerial systems segment is expected to witness considerable growth owing to the factors such as the increasing adoption of drones and UAVs for aerial mapping, which lowers costs and facilitates the collection of data more quickly. Additionally, drones can deliver extremely precise data for surface mapping in locations that are not reachable by satellites.
For instance, in March 2023, Cloudeo, a geospatial solutions provider, announced a partnership with Globhe, a drone-as-a-service company, to expand its range of geospatial products on the Cloudeo marketplace. In addition to satellite and aerial solutions, the partnership included drone data for Cloudeo geospatial offerings. along with user workflows and applications, the partnership also included integrating Globhe drone data and services into answer. Cloudeo's API-based solution for risk evaluation and damage assessment.
The satellite segment is anticipated to register a considerable CAGR over the forecast period. The satellite segment growth in the U.S. can be attributed to the growing number of Earth observation projects undertaken by major space agencies such as the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). The increasing usage of satellite-based photographs for weather forecasting is another factor anticipated to fuel the segment’s growth. Satellites are the most prominent space platforms for remote sensing to collect data from across the globe and track changes in the Earth's atmosphere, oceans, and land. They are also used in national security and catastrophe management.
By Technology
By Application
By Platform
Chapter 1. Introduction
1.1. Research Objective
1.2. Scope of the Study
1.3. Definition
Chapter 2. Research Methodology
2.1. Research Approach
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Assumptions & Limitations
Chapter 3. Executive Summary
3.1. Market Snapshot
Chapter 4. Market Variables and Scope
4.1. Introduction
4.2. Market Classification and Scope
4.3. Industry Value Chain Analysis
4.3.1. Raw Material Procurement Analysis
4.3.2. Sales and Distribution Technology Analysis
4.3.3. Downstream Buyer Analysis
Chapter 5. COVID 19 Impact on U.S. Remote Sensing Technology Market
5.1. COVID-19 Landscape: U.S. Remote Sensing Technology Industry Impact
5.2. COVID 19 - Impact Assessment for the Industry
5.3. COVID 19 Impact: Major Government Policy
5.4. Market Trends and Opportunities in the COVID-19 Landscape
Chapter 6. Market Dynamics Analysis and Trends
6.1. Market Dynamics
6.1.1. Market Drivers
6.1.2. Market Restraints
6.1.3. Market Opportunities
6.2. Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
6.2.1. Bargaining power of suppliers
6.2.2. Bargaining power of buyers
6.2.3. Threat of substitute
6.2.4. Threat of new entrants
6.2.5. Degree of competition
Chapter 7. Competitive Landscape
7.1.1. Company Market Share/Positioning Analysis
7.1.2. Key Strategies Adopted by Players
7.1.3. Vendor Landscape
7.1.3.1. List of Suppliers
7.1.3.2. List of Buyers
Chapter 8. U.S. Remote Sensing Technology Market, By Technology
8.1. U.S. Remote Sensing Technology Market, by Technology, 2024-2033
8.1.1 Active Remote Sensing
8.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
8.1.2. Passive Remote Sensing
8.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
Chapter 9. U.S. Remote Sensing Technology Market, By Application
9.1. U.S. Remote Sensing Technology Market, by Application, 2024-2033
9.1.1. Agriculture & Living Resources
9.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
9.1.2. Military & Intelligence
9.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
9.1.3. Disaster Management
9.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
9.1.4. Infrastructure
9.1.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
9.1.5. Weather
9.1.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
9.1.6. Others
9.1.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
Chapter 10. U.S. Remote Sensing Technology Market, By Platform
10.1. U.S. Remote Sensing Technology Market, by Platform, 2024-2033
10.1.1. Satellite
10.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
10.1.2. Aerial Systems
10.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
Chapter 11. U.S. Remote Sensing Technology Market, Regional Estimates and Trend Forecast
11.1. U.S.
11.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology (2021-2033)
11.1.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application (2021-2033)
11.1.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Platform (2021-2033)
Chapter 12. Company Profiles
12.1. Maxar Technologies
12.1.1. Company Overview
12.1.2. Product Offerings
12.1.3. Financial Performance
12.1.4. Recent Initiatives
12.2. Esri
12.2.1. Company Overview
12.2.2. Product Offerings
12.2.3. Financial Performance
12.2.4. Recent Initiatives
12.3. General Dynamics Mission Systems, Inc.
12.3.1. Company Overview
12.3.2. Product Offerings
12.3.3. Financial Performance
12.3.4. Recent Initiatives
12.4. Hexagon
12.4.1. Company Overview
12.4.2. Product Offerings
12.4.3. Financial Performance
12.4.4. Recent Initiatives
12.5. Lockheed Martin Corporation
12.5.1. Company Overview
12.5.2. Product Offerings
12.5.3. Financial Performance
12.5.4. Recent Initiatives
12.6. Orbital Insight
12.6.1. Company Overview
12.6.2. Product Offerings
12.6.3. Financial Performance
12.6.4. Recent Initiatives
12.7. Planet Labs PBC
12.7.1. Company Overview
12.7.2. Product Offerings
12.7.3. Financial Performance
12.7.4. Recent Initiatives
12.8. Raytheon Technologies Corporation
12.8.1. Company Overview
12.8.2. Product Offerings
12.8.3. Financial Performance
12.8.4. Recent Initiatives
12.9. Teledyne Technologies Incorporated
12.9.1. Company Overview
12.9.2. Product Offerings
12.9.3. Financial Performance
12.9.4. Recent Initiatives
12.10. Leidos
12.10.1. Company Overview
12.10.2. Product Offerings
12.10.3. Financial Performance
12.10.4. Recent Initiatives
Chapter 13. Research Methodology
13.1. Primary Research
13.2. Secondary Research
13.3. Assumptions
Chapter 14. Appendix
14.1. About Us
14.2. Glossary of Terms
 Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
 Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
 Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
 Country/Region-specific Report
Country/Region-specific Report
 Go To Market Strategy
Go To Market Strategy
 Region Specific Market Dynamics
Region Specific Market Dynamics Region Level Market Share
Region Level Market Share Import Export Analysis
Import Export Analysis Production Analysis
Production Analysis Others
Others