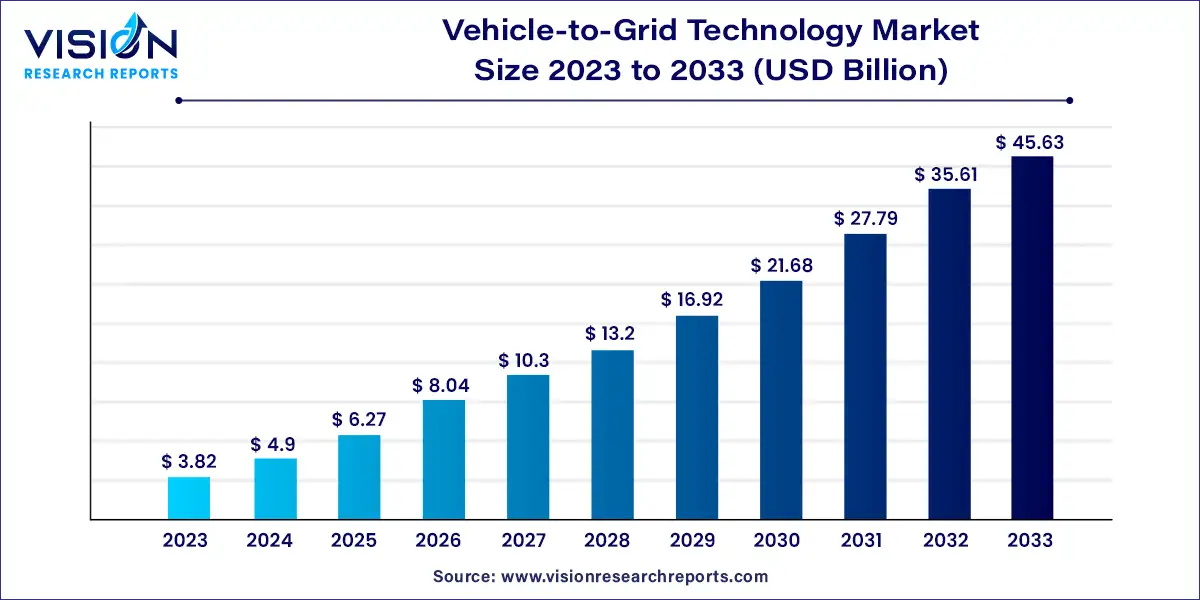
The global vehicle-to-grid technology market size was estimated at around USD 3.82 billion in 2023 and it is projected to hit around USD 45.63 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 28.15% from 2024 to 2033.
Vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology enables bidirectional energy flow between electric vehicles (EVs) and the power grid. This innovative concept allows EVs not only to consume electricity but also to feed surplus energy back to the grid when not in use. By leveraging the energy storage capacity of EV batteries, V2G technology holds immense potential in balancing electricity supply and demand, enhancing grid stability, and facilitating renewable energy integration.
The growth of the vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology market is propelled by an increasing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) worldwide is driving demand for V2G solutions, as these vehicles serve as mobile energy storage units capable of feeding surplus electricity back to the grid. Secondly, advancements in smart grid infrastructure and renewable energy integration are creating opportunities for V2G technology to enhance grid stability and optimize energy utilization. Additionally, supportive government policies and incentives aimed at promoting clean energy and sustainable transportation further stimulate market growth by incentivizing investment in V2G infrastructure. Moreover, collaborations between automotive manufacturers, energy utilities, and technology providers are fostering innovation and driving the development of interoperable V2G solutions.
The electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE) market is projected to surpass the global vehicle-to-grid technology market by 2033. In 2023, EVSE accounted for a significant revenue share of approximately 83%, primarily driven by the increasing utilization of EVSE for connecting electric vehicles to the grid. Serving as the primary component linking EVs to the electric grid, EVSE is poised for increased demand due to the growing trend toward renewable and smart energy generation. EVSE plays a crucial role in both charging electric vehicles and supplying energy back to the grid, thereby driving its segment growth in the forthcoming years.
During approximately 95% of the time when electric vehicles are not in use, vehicle-to-grid technology enables the utilization of stored energy by supplying it back to the grid. This functionality becomes instrumental in meeting electricity demands during peak hours and ensuring continuity of essential or emergency services during blackouts and natural disasters. As such, the significance of EVSE in facilitating bidirectional energy flow between electric vehicles and the grid is expected to drive its market growth in the foreseeable future.
Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) commanded a notable revenue share in the global vehicle-to-grid technology market in 2023. The primary driver behind this segment's substantial growth is its reliance on energy storage systems within the vehicle, enabling it to maximize power return to the grid. A significant milestone in this realm occurred in 2018 when Nissan Motors Co. Ltd. introduced its inaugural electric car, the Nissan Leaf, which obtained regulatory approval for providing power backup to Germany's electric grid. The subsequent pilot project in January 2019 saw the company successfully selling 8 kWh of electricity back to the grid. The exclusive utilization of an energy storage system within the vehicle underscores the rapid expansion of this category, facilitating optimal power redistribution to the grid.
Meanwhile, Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) are anticipated to exhibit the fastest growth throughout the forecast period. Equipped with larger batteries and plug-in chargers capable of powering the vehicle for 20 to 60 miles after just one hour of charging, PHEVs boast significant potential for returning substantial power to the grid. The larger battery size enhances its capacity to contribute significant power back to the grid, translating to greater earnings for vehicle owners. Moreover, the increasing favorability of PHEVs, attributed to their user-friendly features and advantageous benefits compared to BEVs, is poised to drive market growth in the foreseeable future.
Both North America and Europe emerged as key regions in the global vehicle-to-grid technology market, making substantial revenue contributions in 2023. Government initiatives aimed at curbing carbon emissions by promoting the use of battery-powered vehicles stand as primary drivers propelling market growth. Additionally, manufacturers offering long-term warranties and government subsidies and benefits for electric vehicle adoption attract a sizable consumer base.
Conversely, the Asia Pacific region anticipates lucrative growth in the vehicle-to-grid technology market over the forecast period. This growth is fueled by green revolution drives in countries such as China, Japan, India, and South Korea. Notably, China has set a vision for fully electric-powered mobility in the region by 2025 and is making significant investments to achieve this goal.
Recent developments in automobile batteries have led to longer operational lifespans and increased durability against repeated charging cycles. Moreover, the introduction of vehicle-to-everything technology, as an extension of vehicle-to-grid technology, with smaller sizes, lighter weights, and simplified installation processes, is driving market expansion. The market is poised to benefit from extensive infrastructural developments and the implementation of favorable government policies that promote smart grid initiatives.
By Component Type
By Application Type
By Region
 Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
 Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
 Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
 Country/Region-specific Report
Country/Region-specific Report
 Go To Market Strategy
Go To Market Strategy
 Region Specific Market Dynamics
Region Specific Market Dynamics Region Level Market Share
Region Level Market Share Import Export Analysis
Import Export Analysis Production Analysis
Production Analysis Others
Others